Drosophila Thor participates in host immune defense and connects a translational regulator with innate immunity
- PMID: 10811906
- PMCID: PMC18551
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.100391597
Drosophila Thor participates in host immune defense and connects a translational regulator with innate immunity
Abstract
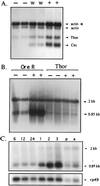
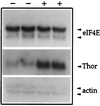
Thor has been identified as a new type of gene involved in Drosophila host immune defense. Thor is a member of the 4E-binding protein (4E-BP) family, which in mammals has been defined as critical regulators in a pathway that controls initiation of translation through binding eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E). Without an infection, Thor is expressed during all developmental stages and transcripts localize to a wide variety of tissues, including the reproductive system. In response to bacterial infection and, to a lesser extent, by wounding, Thor is up-regulated. The Thor promoter has the canonical NFkappaB and associated GATA recognition sequences that have been shown to be essential for immune induction, as well as other sequences commonly found for Drosophila immune response genes, including interferon-related regulatory sequences. In survival tests, Thor mutants show symptoms of being immune compromised, indicating that Thor may be critical in host defense. In contrast to Thor, Drosophila eIF4E is not induced by bacterial infection. These findings for Thor provide the first evidence that a 4E-BP family member has a role in immune induction in any organism. Further, no gene in the translation initiation pathway that includes 4E-BP has been previously found to be immune induced. Our results suggest either a role for translational regulation in humoral immunity or a new, nontranslational function for 4E-BP type genes.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

