Adhesion molecule deficiencies increase Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced alveolar bone loss in mice
- PMID: 10816450
- PMCID: PMC97538
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.6.3103-3107.2000
Adhesion molecule deficiencies increase Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced alveolar bone loss in mice
Abstract
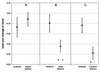
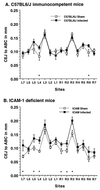
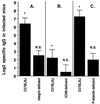
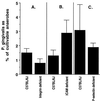
Alveolar bone resorption can be induced in specific-pathogen-free mice by oral infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. J. Baker, R. T. Evans, and D. C. Roopenian, Arch. Oral Biol. 39:1035-1040, 1994). Here we used a mouse strain, C57BL/6J, which is relatively resistant to P. gingivalis-induced bone loss to examine whether partial or complete deletion of various adhesion molecules would increase susceptibility. Complete deletion of P-selectin or nearly complete lack of expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) led to increased susceptibility to bone resorption after oral infection, while a hypomorphic defect in beta(2)-integrins did not. Both the total amount of bone lost and the number of sites at which there was significant loss were increased in mice deficient in either ICAM-1 or P-selectin. Each of the three adhesion molecule deficiencies was sufficient to decrease P. gingivalis-specific serum immunoglobulin G responses, but lower antibody titers did not lead to increased bone loss in partially beta(2)-integrin-deficient mice. In conclusion, P-selectin and ICAM-1 deficiencies increase susceptibility to and severity of alveolar bone loss after P. gingivalis infection. This finding underscores the importance of innate immunity in protection against P. gingivalis-induced alveolar bone resorption.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson D C, Miller L J, Schmalstieg F C, Rothlein R, Springer T A. Contributions of the Mac-1 glycoprotein family to adherence dependent granulocyte functions: structure-function assessments employing subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1986;137:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Baker P J, Evans R T, Roopenian D C. Oral infection with Porphyromonas gingivalis and induced alveolar bone loss in immunocompetent and severe combined immunodeficient mice. Arch Oral Biol. 1994;39:1035–1040. - PubMed
-
- Baker P J, Carter S, Dixon M, Evans R T, Roopenian D C. Serum antibody response to oral infection precedes but does not prevent Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced alveolar bone loss in mice. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1999;14:194–196. - PubMed
-
- Bertolini D R, Nedwin T, Bringman T, Smith D, Mundy G R. Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumour necrosis factors. Nature. 1985;319:516–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

