Streptococcal erythrogenic toxin B abrogates fibronectin-dependent internalization of Streptococcus pyogenes by cultured mammalian cells
- PMID: 10816467
- PMCID: PMC97567
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.6.3226-3232.2000
Streptococcal erythrogenic toxin B abrogates fibronectin-dependent internalization of Streptococcus pyogenes by cultured mammalian cells
Abstract
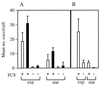
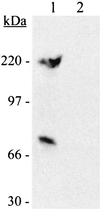
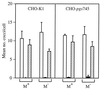
Streptococcus pyogenes secretes several proteins that influence host-pathogen interactions. A tissue-culture model was used to study the influence of the secreted cysteine protease streptococcal erythrogenic toxin B (SPE B) on the interaction between S. pyogenes strain NZ131 (serotype M49) and mammalian cells. Inactivation of the speB gene enhanced fibronectin-dependent uptake of the pathogen by Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells compared to that in the isogenic wild-type strain. Preincubation of the NZ131 speB mutant with purified SPE B protease significantly inhibited fibronectin-dependent uptake by both CHO-K1 and CHO-pgs745 cells. The effect was attributed to an abrogation of fibronectin binding to the surface of the bacteria that did not involve either the M49 protein or the streptococcal fibronectin-binding protein SfbI. In contrast, pretreatment of the NZ131 speB mutant with SPE B did not influence sulfated polysaccharide-mediated uptake by CHO-pgs745 cells. The results indicate that the SPE B protease specifically alters bacterial cell surface proteins and thereby influences pathogen uptake.
Figures

References
-
- Berge A, Björck L. Streptococcal cysteine proteinase releases biologically active fragments of streptococcal surface proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:9862–9867. - PubMed
-
- Björck L, Åkesson P, Bohus M, Trojnar J, Abrahamson M, Olafsson I, Grubb A. Bacterial growth blocked by a synthetic peptide based on the structure of a human proteinase inhibitor. Nature. 1989;337:385–386. - PubMed
-
- Burns E H, Jr, Lukomski S, Rurangirwa J, Podbielski A, Musser J M. Genetic inactivation of the extracellular cysteine protease enhances in vitro internalization of group A streptococci by human epithelial and endothelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1998;24:333–339. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

