Monitoring bioluminescent Staphylococcus aureus infections in living mice using a novel luxABCDE construct
- PMID: 10816517
- PMCID: PMC97648
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.6.3594-3600.2000
Monitoring bioluminescent Staphylococcus aureus infections in living mice using a novel luxABCDE construct
Abstract
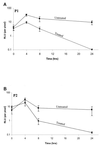
Strains of Staphylococcus aureus were transformed with plasmid DNA containing a Photorhabdus luminescens lux operon (luxABCDE) that was genetically modified to be functional in both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. S. aureus cells containing this novel lux construct, downstream of an appropriate promoter sequence, are highly bioluminescent, allowing the detection of fewer than 100 CFU in vitro (direct detection of exponentially dividing cells in liquid culture). Furthermore, these bacteria produce light stably at 37 degrees C and do not require exogenous aldehyde substrate, thus allowing S. aureus infections in living animals to be monitored by bioluminescence. Two strains of S. aureus 8325-4 that produce high levels of constitutive bioluminescence were injected into the thigh muscles of mice, and the animals were then either treated with the antibiotic amoxicillin or left untreated. Bioluminescence from bacteria present in the thighs of the mice was monitored in vivo over a period of 24 h. The effectiveness of the antibiotic in the treated animals could be measured by a decrease in the light signal. At 8 h, the infection in both groups of treated animals had begun to clear, as judged by a decrease in bioluminescence, and by 24 h no light signal could be detected. In contrast, both groups of untreated mice had strong bioluminescent signals at 24 h. Quantification of CFU from bacteria extracted from the thigh muscles of the mice correlated well with the bioluminescence data. This paper shows for the first time that bioluminescence offers a method for monitoring S. aureus infections in vivo that is sensitive and noninvasive and requires fewer animals than conventional methodologies.
Figures




References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. Vol. 1. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1995.
-
- Boemare N E, Akhhurst R J, Mourant R G. DNA relatedness between Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae), symbiotic bacteria of entomopathogenic nematodes, and a proposal to transfer Xenorhabdus luminescens to a new genus, Photorhabdus gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993;43:249–255.
-
- Carbon C. Costs of treating infections caused by methicillin-resistant staphylococci and vancomycin-resistant enterococci. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1999;44:31–36. - PubMed
-
- Contag C H, Contag P R, Mullins J I, Spilman S D, Stevenson D K, Benaron D A. Photonic detection of bacterial pathogens in living hosts. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:593–603. - PubMed
-
- Corbisier P, Ji G, Nuyts G, Mergeay M, Silver S. luxAB gene fusions with the arsenic and cadmium resistance operons of Staphylococcus aureus plasmid pI258. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993;110:231–238. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

