mu-Opioid receptors often colocalize with the substance P receptor (NK1) in the trigeminal dorsal horn
- PMID: 10818170
- PMCID: PMC6772648
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-11-04345.2000
mu-Opioid receptors often colocalize with the substance P receptor (NK1) in the trigeminal dorsal horn
Abstract
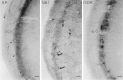
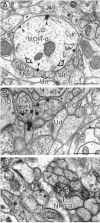
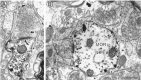
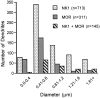
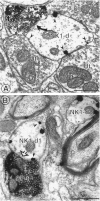
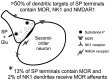
Substance P (SP) is a peptide that is present in unmyelinated primary afferents to the dorsal horn and is released in response to painful or noxious stimuli. Opiates active at the mu-opiate receptor (MOR) produce antinociception, in part, through modulation of responses to SP. MOR ligands may either inhibit the release of SP or reduce the excitatory responses of second-order neurons to SP. We examined potential functional sites for interactions between SP and MOR with dual electron microscopic immmunocytochemical localization of the SP receptor (NK1) and MOR in rat trigeminal dorsal horn. We also examined the relationship between SP-containing profiles and NK1-bearing profiles. We found that 56% of SP-immunoreactive terminals contact NK1 dendrites, whereas 34% of NK1-immunoreactive dendrites receive SP afferents. This result indicates that there is not a significant mismatch between sites of SP release and available NK1 receptors, although receptive neurons may contain receptors at sites distant from the peptide release site. With regard to opioid receptors, we found that many MOR-immunoreactive dendrites also contain NK1 (32%), whereas a smaller proportion of NK1-immunoreactive dendrites contain MOR (17%). Few NK1 dendrites (2%) were contacted by MOR-immunoreactive afferents. These results provide the first direct evidence that MORs are on the same neurons as NK1 receptors, suggesting that MOR ligands directly modulate SP-induced nociceptive responses primarily at postsynaptic sites, rather than through inhibition of SP release from primary afferents. This colocalization of NK1 and MORs has significant implications for the development of pain therapies targeted at these nociceptive neurons.
Figures



References
-
- Aicher SA, Reis DJ, Nicolae R, Milner TA. Monosynaptic projections from the medullary gigantocellular reticular formation to sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the thoracic spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1995;363:563–580. - PubMed
-
- Aicher SA, Saravay RH, Cravo SL, Jeske I, Morrison SF, Reis DJ, Milner TA. Monosynaptic projections from the nucleus tractus solitarii to C1 adrenergic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla: comparison with input from the caudal ventrolateral medulla. J Comp Neurol. 1996;373:62–75. - PubMed
-
- Aicher SA, Sharma S, Cheng PY, Pickel VM. The N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor is postsynaptic to substance P-containing axon terminals in the rat superficial dorsal horn. Brain Res. 1997;772:71–81. - PubMed
-
- Aicher SA, Sharma S, Cheng PY, Liu-Chen LY, Pickel VM. Dual ultrastructural localization of μ-opiate receptors and substance P in the dorsal horn. Synapse. 2000;36:12–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
