A potent dimeric peptide antagonist of interleukin-5 that binds two interleukin-5 receptor alpha chains
- PMID: 10823900
- PMCID: PMC18766
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.110053997
A potent dimeric peptide antagonist of interleukin-5 that binds two interleukin-5 receptor alpha chains
Abstract
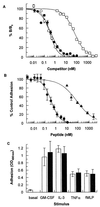
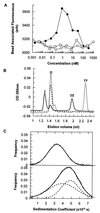
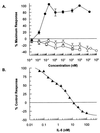
Two series of peptides that specifically bind to the extracellular domain of the alpha chain of the human interleukin-5 receptor (IL-5Ralpha), but share no primary sequence homology to IL-5, were identified from libraries of random recombinant peptides. Affinity maturation procedures generated a 19-aa peptide that binds to the IL-5 receptor alpha/beta heterodimer complex with an affinity equal to that of IL-5 and is a potent and specific antagonist of IL-5 activity in a human eosinophil adhesion assay. The active form of the peptide is a disulfide-crosslinked dimer that forms spontaneously in solution. Gel filtration analysis, receptor-binding studies, and analytical ultracentrifugation reveal that the dimeric peptide binds simultaneously to two receptor alpha chains in solution. Furthermore, the dimer peptide, but not IL-5, can activate a chimeric receptor consisting of the IL-5Ralpha extracellular domain fused to the intracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor, thus demonstrating that the peptide also promotes receptor dimerization in a cellular context. The functional antagonism produced by the bivalent interaction of the dimeric peptide with two IL-5R alpha chains represents a distinctive mechanism for the antagonism of cytokines that use heteromeric receptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional analysis of the interleukin-5 receptor antagonist peptide, AF18748.Cytokine. 2004 Jun 21;26(6):247-54. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2003.10.012. Cytokine. 2004. PMID: 15183842
-
Cyclic peptide interleukin 5 antagonists mimic CD turn recognition epitope for receptor alpha.Biopolymers. 2004 Apr 5;73(5):556-68. doi: 10.1002/bip.20001. Biopolymers. 2004. PMID: 15048779
-
Simultaneous antagonism of interleukin-5, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and interleukin-3 stimulation of human eosinophils by targetting the common cytokine binding site of their receptors.Blood. 1999 Sep 15;94(6):1943-51. Blood. 1999. PMID: 10477723
-
Role of the interleukin 5 receptor system in hematopoiesis: molecular basis for overlapping function of cytokines.Bioessays. 1992 Aug;14(8):527-33. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140806. Bioessays. 1992. PMID: 1365906 Review.
-
Cytokine recognition by human interleukin 5 receptor.Vitam Horm. 2005;71:321-44. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(05)71011-6. Vitam Horm. 2005. PMID: 16112273 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of cyclic peptides able to mimic the functional epitope of IgG1-Fc for human Fc gammaRI.FASEB J. 2009 Feb;23(2):575-85. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-117069. Epub 2008 Oct 28. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 18957574 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric usage of antagonist charged residues drives interleukin-5 receptor recruitment but is insufficient for receptor activation.Biochemistry. 2006 Jan 31;45(4):1106-15. doi: 10.1021/bi0518038. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16430207 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine regulation of asthmatic airway inflammation: role of airway smooth muscle.Respir Res. 2002;3(1):11. doi: 10.1186/rr160. Epub 2001 Nov 28. Respir Res. 2002. PMID: 11806846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-5 receptor subunit oligomerization and rearrangement revealed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer imaging.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 9;283(19):13398-406. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M710230200. Epub 2008 Mar 7. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18326494 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic multivalent ligands as probes of signal transduction.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2006 Apr 3;45(15):2348-68. doi: 10.1002/anie.200502794. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2006. PMID: 16557636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sanderson C J. Blood. 1992;79:3101–3109. - PubMed
-
- Denburg J A, Silver J E, Abrams J S. Blood. 1991;77:1462–1468. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi Y, Suda T, Ohta S, Tominaga K, Miura Y, Kasahara T. Blood. 1991;78:2542–2547. - PubMed
-
- Fujisawa T, Abu-Ghazaleh R, Kita H, Sanderson C J, Gleich G J. J Immunol. 1990;144:642–646. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

