Phylogenetic relationships of Cryptosporidium parasites based on the 70-kilodalton heat shock protein (HSP70) gene
- PMID: 10831415
- PMCID: PMC110539
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.6.2385-2391.2000
Phylogenetic relationships of Cryptosporidium parasites based on the 70-kilodalton heat shock protein (HSP70) gene
Abstract
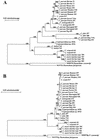
We have characterized the nucleotide sequences of the 70-kDa heat shock protein (HSP70) genes of Cryptosporidium baileyi, C. felis, C. meleagridis, C. muris, C. serpentis, C. wrairi, and C. parvum from various animals. Results of the phylogenetic analysis revealed the presence of several genetically distinct species in the genus Cryptosporidium and eight distinct genotypes within the species C. parvum. Some of the latter may represent cryptic species. The phylogenetic tree constructed from these sequences is in agreement with our previous results based on the small-subunit rRNA genes of Cryptosporidium parasites. The Cryptosporidium species formed two major clades: isolates of C. muris and C. serpentis formed the first major group, while isolates of C. felis, C. meleagridis, C. wrairi, and eight genotypes of C. parvum formed the second major group. Sequence variations were also observed between C. muris isolates from ruminants and rodents. The HSP70 gene provides another useful locus for phylogenetic analysis of the genus Cryptosporidium.
Figures


References
-
- Arrowood M J, Sterling C R. Isolation of Cryptosporidium oocysts and sporozoites using discontinuous sucrose and isopycnic Percoll gradients. J Parasitol. 1987;73:314–319. - PubMed
-
- Awad-El-Kariem F A, Warhurst D C, McDonald V. Detection of Cryptosporidium oocysts using a system based on PCR and endonuclease restriction. Parasitology. 1994;109:19–22. - PubMed
-
- Budin K, Philippe H. New insights into the phylogeny of eukaryotes based on ciliate Hsp70 sequences. Mol Biol Evol. 1998;15:943–956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

