Use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA as a means of developing genus- and strain-specific Streptomyces DNA probes
- PMID: 10831438
- PMCID: PMC110581
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.6.2555-2564.2000
Use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA as a means of developing genus- and strain-specific Streptomyces DNA probes
Abstract
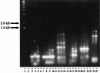
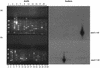
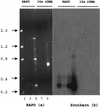
We have analyzed 20 randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) primers against 36 Streptomyces strains, including 17 taxonomically undefined strains, 25 nonstreptomycete actinomycetes, and 12 outgroups consisting of gram-positive and -negative species. Most of the primers were useful in identifying unique DNA polymorphisms of all strains tested. We have used RAPD techniques to develop a genus-specific probe, one not necessarily targeting the ribosomal gene, for Streptomyces, and a strain-specific probe for the biological control agent Streptomyces lydicus WYEC108. In the course of these investigations, small-scale DNA isolations were also developed for efficiently isolating actinomycete DNA. Various modifications of isolation procedures for soil DNA were compared, and the reliability and specificity of the RAPD methodology were tested by specifically detecting the S. lydicus WYEC108 in DNA isolated from soil.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and typing of Streptomyces strains: evaluation of interspecific, intraspecific and intraclonal differences by RAPD fingerprinting.Res Microbiol. 2000 Dec;151(10):853-64. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2508(00)01152-9. Res Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11191811
-
Use of RAPD-PCR fingerprinting to detect genetic diversity of soil Streptomyces isolates.New Microbiol. 1999 Jan;22(1):53-8. New Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10190117
-
Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of antibiotic-producing soil Streptomyces investigated by RAPD-PCR.J Basic Microbiol. 2003;43(1):18-27. doi: 10.1002/jobm.200390000. J Basic Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12596238
-
Application of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) assays in identifying conserved regions of actinomycete genomes.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995 May 1;128(2):119-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07510.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1995. PMID: 7750729
-
Use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) for generating specific DNA probes for microorganisms.Mol Ecol. 1993 Aug;2(4):243-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294x.1993.tb00014.x. Mol Ecol. 1993. PMID: 8167854
Cited by
-
Phenotypic and molecular analysis of dominant occurring antibiotic active-producing Streptomyces soil flora in Northern Jordan.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Aug;28(8):4500-4510. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.04.048. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34354436 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging strategies and integrated systems microbiology technologies for biodiscovery of marine bioactive compounds.Mar Drugs. 2014 Jun 10;12(6):3516-59. doi: 10.3390/md12063516. Mar Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24918453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Latitudinal Diversity Gradient in Terrestrial Bacteria of the Genus Streptomyces.mBio. 2016 Apr 12;7(2):e02200-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02200-15. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27073097 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic conservatism of thermal traits explains dispersal limitation and genomic differentiation of Streptomyces sister-taxa.ISME J. 2018 Sep;12(9):2176-2186. doi: 10.1038/s41396-018-0180-3. Epub 2018 Jun 7. ISME J. 2018. PMID: 29880909 Free PMC article.
-
Streptomyces sp. strain SK68, isolated from peanut rhizosphere, promotes growth and alleviates salt stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum cv. Micro-Tom).J Microbiol. 2018 Oct;56(10):753-759. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-8120-5. Epub 2018 Sep 28. J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30267318
References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Short protocols in molecular biology. 2nd ed. New York, N.Y: Green Publishing Associates/John Wiley & Sons; 1992.
-
- Beyazova M, Lechevalier M P. Taxonomic utility of restriction endonuclease fingerprinting of large DNA fragments from Streptomyces strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993;43:674–682.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

