Microbiological transformation of enrofloxacin by the fungus Mucor ramannianus
- PMID: 10831454
- PMCID: PMC110597
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.66.6.2664-2667.2000
Microbiological transformation of enrofloxacin by the fungus Mucor ramannianus
Abstract
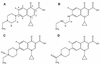
Enrofloxacin metabolism by Mucor ramannianus was investigated as a model for the biotransformation of veterinary fluoroquinolones. Cultures grown in sucrose-peptone broth were dosed with enrofloxacin. After 21 days, 22% of the enrofloxacin remained. Three metabolites were identified: enrofloxacin N-oxide (62% of the total absorbance), N-acetylciprofloxacin (8.0%), and desethylene-enrofloxacin (3.5%).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microbial transformations of antimicrobial quinolones and related drugs.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Dec;39(12):1731-40. doi: 10.1007/s10295-012-1194-x. Epub 2012 Sep 25. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23007957 Review.
-
Metabolism of the veterinary fluoroquinolone sarafloxacin by the fungus Mucor ramannianus.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Mar;26(3):140-4. doi: 10.1038/sj.jim.7000077. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11420653
-
Regioselective transformation of ciprofloxacin to N-acetylciprofloxacin by the fungus Mucor ramannianus.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999 Aug 1;177(1):131-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13723.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999. PMID: 10436931
-
Degradation of the fluoroquinolone enrofloxacin by the brown rot fungus Gloeophyllum striatum: identification of metabolites.Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997 Nov;63(11):4272-81. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.11.4272-4281.1997. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9361414 Free PMC article.
-
Disposition of single-dose oral enrofloxacin in the horse.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1996 Aug;19(4):316-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.1996.tb00057.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1996. PMID: 8866463 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Microbial transformations of antimicrobial quinolones and related drugs.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Dec;39(12):1731-40. doi: 10.1007/s10295-012-1194-x. Epub 2012 Sep 25. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23007957 Review.
-
The Umbelopsis ramanniana Sensu Lato Consists of Five Cryptic Species.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Aug 23;8(9):895. doi: 10.3390/jof8090895. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36135620 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of ciprofloxacin-conjugated poly (L-lactic acid) polymer for nanofiber fabrication and antibacterial evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 Mar 26;9:1463-77. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S54971. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24741303 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of metabolites produced from N-phenylpiperazine by Mycobacterium spp.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007 Mar;34(3):219-24. doi: 10.1007/s10295-006-0189-x. Epub 2006 Dec 22. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2007. PMID: 17186210
-
Transformation of N-phenylpiperazine by mixed cultures from a municipal wastewater treatment plant.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Oct;74(19):6147-50. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00516-08. Epub 2008 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18676696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azerad R. Microbial models for drug metabolism. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 1999;63:169–218. - PubMed
-
- Barrow P A, Lovell M A, Szmolleny G, Murphy C K. Effect of enrofloxacin administration on excretion of Salmonella enteritidis by experimentally infected chickens and on quinolone resistance of their Escherichia coli flora. Avian Pathol. 1998;27:586–590. - PubMed
-
- Borner K, Borner E, Hartwig H, Lode H. HPLC of recent quinolone antimicrobials. In: Reid E, Wilson I D, editors. Analysis for drugs and metabolites, including anti-infective agents. Cambridge, England: Royal Society of Chemistry; 1990. pp. 131–144.
-
- Brown S A. Fluoroquinolones in animal health. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 1996;19:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Cerniglia C E, Hansen E B, Jr, Lambert K J, Korfmacher W A, Miller D W. Fungal transformations of antihistamines: metabolism of methapyrilene, thenyldiamine and tripelennamine to N-oxide and N-demethylated derivatives. Xenobiotica. 1988;18:301–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

