A multicenter study evaluation of the digene hybrid capture II signal amplification technique for detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum samples and testing of EUROHEP standards
- PMID: 10834968
- PMCID: PMC86750
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.38.6.2150-2155.2000
A multicenter study evaluation of the digene hybrid capture II signal amplification technique for detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum samples and testing of EUROHEP standards
Abstract
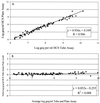
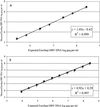
We have evaluated the new Digene Hybrid Capture II HBV DNA Test (HCII HBV), which is a 96-well microtiter plate-based signal amplification assay. This test uses hybrid capture technology that specifically detects RNA-DNA hybrids. HCII HBV is able to quantify hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA at between 1.4 x 10(5) and 1.7 x 10(9) HBV copies per ml in a standard format. By using a modified sample preparation method, which allows the input of 30-fold more serum for an ultrasensitive format, the sensitivity of the assay can be increased reproducibly to approximately 8,000 copies of HBV per ml. By using a combination of these two formats, the assay can quantify over a total range of 6 logs. In our multicenter evaluation study, the mean laboratory-to-laboratory coefficients of variation were 22, 7, and 12% at the three sites, respectively, with a combined specificity of 98.4%. The linearities of both the standard test and the ultrasensitive test were excellent, with Spearman correlation coefficients of 0.997 and 0.999, respectively. Furthermore, the intra-assay reproducibility for the standard assay gave coefficients of variation of from 13 to 33, 9 to 21, and 3 to 8% at the three sites, respectively. HCII HBV was shown to be genotype independent when the EUROHEP standards for genotypes A and D were used. This assay allows the accurate measurement of HBV DNA levels in serum and can be clinically used for the monitoring of responses to antiviral agents for patients chronically infected with HBV.
Figures


References
-
- Bland J M, Altman D G. Comparing methods of measurement: why plotting difference against standard method is misleading. Lancet. 1995;346:1085–1087. - PubMed
-
- Bresters D, Cuypers H T, Reesink H W, Mauser-Bunschoten E P, van den Berg H M, Schaasberg W P, Wilber J C, Urdea M S, Neuwald P, Lelie P N. Comparison of quantitative cDNA-PCR with the branched DNA hybridization assay for monitoring plasma hepatitis C virus RNA levels in haemophilia patients participating in a controlled interferon trial. J Med Virol. 1994;43:262–268. - PubMed
-
- Butterworth L A, Prior S L, Buda P J, Faoagali J L, Cooksley W G. Comparison of four methods for quantitative measurement of hepatitis B viral DNA. J Hepatol. 1996;24:686–691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

