Structural basis for recognition of the translocated intimin receptor (Tir) by intimin from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 10835344
- PMCID: PMC212744
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.11.2452
Structural basis for recognition of the translocated intimin receptor (Tir) by intimin from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
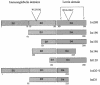
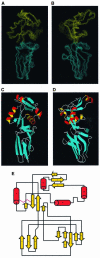
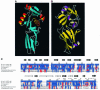
Intimin is a bacterial adhesion molecule involved in intimate attachment of enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli to mammalian host cells. Intimin targets the translocated intimin receptor (Tir), which is exported by the bacteria and integrated into the host cell plasma membrane. In this study we localized the Tir-binding region of intimin to the C-terminal 190 amino acids (Int190). We have also determined the region's high-resolution solution structure, which comprises an immunoglobulin domain that is intimately coupled to a novel C-type lectin domain. This fragment, which is necessary and sufficient for Tir interaction, defines a new super domain in intimin that exhibits striking structural similarity to the integrin-binding domain of the Yersinia invasin and C-type lectin families. The extracellular portion of intimin comprises an articulated rod of immunoglobulin domains extending from the bacterium surface, conveying a highly accessible 'adhesive tip' to the target cell. The interpretation of NMR-titration and mutagenesis data has enabled us to identify, for the first time, the binding site for Tir, which is located at the extremity of the Int190 moiety.
Figures


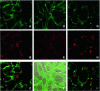
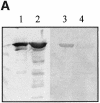

References
-
- Bax A., Clore,G.M. and Gronenborn,A.M.J. (1990) 1H-1H correlation via isotropic mixing of 13C magnetization, a new three-dimensional approach for assigning 1H and 13C spectra of 13C enriched proteins. Magn. Res., 88, 425–431.
-
- Boyington J.G., Riaz,A.N., Patamawam,A., Coligan,J.E., Brook,A.G. and Sun,P.D. (1999) Structure of the CD94 reveals a novel C-type lectin fold: implications for the NK cell-associated CD94/NKG2 receptors. Immunity, 10, 75–82. - PubMed
-
- Brünger A.T. (1993) X_PLOR Manual. Version 3.1. Yale University Press, New Haven, CT.
-
- Cornilescu G., Delaglio,F. and Bax,A. (1999) Protein backbone angle restraints from searching a database for chemical shift and sequence homology. J. Biomol. NMR, 13, 289–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

