Promiscuous targeting of Bacillus subtilis cell division protein DivIVA to division sites in Escherichia coli and fission yeast
- PMID: 10835369
- PMCID: PMC212753
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.11.2719
Promiscuous targeting of Bacillus subtilis cell division protein DivIVA to division sites in Escherichia coli and fission yeast
Erratum in
- EMBO J 2000 Sep 15;19(18):5039
Abstract
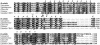
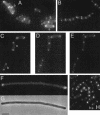
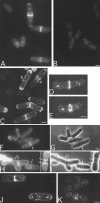
The Bacillus subtilis divIVA gene encodes a coiled-coil protein that shows weak similarity to eukaryotic tropomyosins. The protein is targeted to the sites of cell division and mature cell poles where, in B.subtilis, it controls the site specificity of cell division. Although clear homologues of DivIVA are present only in Gram-positive bacteria, and its role in division site selection is not conserved in the Gram-negative bacterium, Escherichia coli, a DivIVA-green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion was targeted accurately to division sites and retained at the cell pole in this organism. Remarkably, the same fusion protein was also targeted to nascent division sites and growth zones in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, mimicking the localization of the endogenous tropomyosin-like cell division protein Cdc8p, and F-actin. The results show that a targeting signal for division sites is conserved across the eukaryote-prokaryote divide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polar localization of the MinD protein of Bacillus subtilis and its role in selection of the mid-cell division site.Genes Dev. 1998 Nov 1;12(21):3419-30. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.21.3419. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9808628 Free PMC article.
-
Division site selection protein DivIVA of Bacillus subtilis has a second distinct function in chromosome segregation during sporulation.Genes Dev. 2001 Jul 1;15(13):1662-73. doi: 10.1101/gad.197501. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11445541 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular architecture mediates DivIVA ultrastructure and regulates min activity in Bacillus subtilis.mBio. 2011 Nov 22;2(6):e00257-11. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00257-11. Print 2011. mBio. 2011. PMID: 22108385 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for interaction of DivIVA/GpsB proteins with their ligands.Mol Microbiol. 2019 Jun;111(6):1404-1415. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14244. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Mol Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30887576 Review.
-
A mechanism for polar protein localization in bacteria.J Mol Biol. 2004 Jan 9;335(2):655-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.058. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14672671 Review.
Cited by
-
EF1025, a Hypothetical Protein From Enterococcus faecalis, Interacts With DivIVA and Affects Cell Length and Cell Shape.Front Microbiol. 2020 Feb 12;11:83. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00083. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32117116 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomerization and higher-order assembly contribute to sub-cellular localization of a bacterial scaffold.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Nov;90(4):776-95. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12398. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24102805 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Dissection of DivIVA Functions in Listeria monocytogenes.J Bacteriol. 2017 Nov 14;199(24):e00421-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00421-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28972021 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-protein interaction domains of Bacillus subtilis DivIVA.J Bacteriol. 2013 Mar;195(5):1012-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.02171-12. Epub 2012 Dec 21. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23264578 Free PMC article.
-
Making a point: the role of DivIVA in streptococcal polar anatomy.J Bacteriol. 2007 Feb;189(4):1185-8. doi: 10.1128/JB.01710-06. Epub 2006 Nov 17. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17114258 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Addinall S.G. and Lutkenhaus,J. (1996) FtsZ-spirals and -arcs determine the shape of the invaginating septa in some mutants of Escherichia coli.Mol. Microbiol., 22, 231–237. - PubMed
-
- Arai R., Nakano,K. and Mabuchi,I. (1998) Subcellular localization and possible function of actin, tropomyosin and actin-related protein 3 (Arp3) in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Eur. J. Cell Biol., 76, 288–295. - PubMed
-
- Ayscough K.R., Stryker,J., Pokala,N., Sanders,M., Crews,P. and Drubin,D.G. (1997) High rates of actin filament turnover in budding yeast and roles for actin in establishment and maintenance of cell polarity revealed using the actin inhibitor latrunculin-A. J. Cell Biol., 137, 399–416. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian M.K., Helfman,D.M. and Hemmingsen,S.M. (1992) A new tropomyosin essential for cytokinesis in the fission yeast S.pombe.Nature, 360, 84–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

