Notch signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice
- PMID: 10837027
- PMCID: PMC316662
Notch signaling is essential for vascular morphogenesis in mice
Abstract
The Notch gene family encodes large transmembrane receptors that are components of an evolutionarily conserved intercellular signaling mechanism. To assess the role of the Notch4 gene, we generated Notch4-deficient mice by gene targeting. Embryos homozygous for this mutation developed normally, and homozygous mutant adults were viable and fertile. However, the Notch4 mutation displayed genetic interactions with a targeted mutation of the related Notch1 gene. Embryos homozygous for mutations of both the Notch4 and Notch1 genes often displayed a more severe phenotype than Notch1 homozygous mutant embryos. Both Notch1 mutant and Notch1/Notch4 double mutant embryos displayed severe defects in angiogenic vascular remodeling. Analysis of the expression patterns of genes encoding ligands for Notch family receptors indicated that only the Dll4 gene is expressed in a pattern consistent with that expected for a gene encoding a ligand for the Notch1 and Notch4 receptors in the early embryonic vasculature. These results reveal an essential role for the Notch signaling pathway in regulating embryonic vascular morphogenesis and remodeling, and indicate that whereas the Notch4 gene is not essential during embryonic development, the Notch4 and Notch1 genes have partially overlapping roles during embryogenesis in mice.
Figures
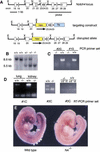
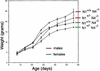
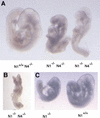
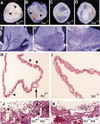
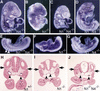
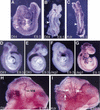
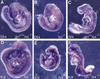
References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin HS, Shen HM, Yan HC, De Lisser HM, Chung A, Mickanin C, Trask T, Kirschbaum NE, Newman PJ, Albeda SM, Buck CA. Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1/CD31): Alternatively spliced, functionally distinct isoforms expressed during mammalian cardiovascular development. Development. 1994;120:2539–2553. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Collen D. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in vascular development. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999;237:133–158. - PubMed
-
- Chan Y-M, Jan YN. Roles for proteolysis and trafficking in Notch maturation and signal transduction. Cell. 1998;94:423–426. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
