Novel HOXA13 mutations and the phenotypic spectrum of hand-foot-genital syndrome
- PMID: 10839976
- PMCID: PMC1287077
- DOI: 10.1086/302961
Novel HOXA13 mutations and the phenotypic spectrum of hand-foot-genital syndrome
Abstract
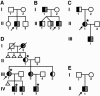
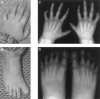
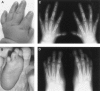
Hand-foot-genital syndrome (HFGS) is a rare, dominantly inherited condition affecting the distal limbs and genitourinary tract. A nonsense mutation in the homeobox of HOXA13 has been identified in one affected family, making HFGS the second human syndrome shown to be caused by a HOX gene mutation. We have therefore examined HOXA13 in two new and four previously reported families with features of HFGS. In families 1, 2, and 3, nonsense mutations truncating the encoded protein N-terminal to or within the homeodomain produce typical limb and genitourinary abnormalities; in family 4, an expansion of an N-terminal polyalanine tract produces a similar phenotype; in family 5, a missense mutation, which alters an invariant domain, produces an exceptionally severe limb phenotype; and in family 6, in which limb abnormalities were atypical, no HOXA13 mutation could be detected. Mutations in HOXA13 can therefore cause more-severe limb abnormalities than previously suspected and may act by more than one mechanism.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Web/GenBank (for the sequence of HOXA13 [U82827])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for HFGS [MIM 140000] and for synpolydactyly [MIM 186000])
References
-
- Akarsu AN, Stoilov I, Yilmaz E, Sayli BS, Sarfarazi M (1996) Genomic structure of HOXD13 gene: a nine polyalanine duplication causes synpolydactyly in two unrelated families. Hum Mol Genet 5:945–952 - PubMed
-
- Brown SA, Warburton D, Brown LY, Yu C, Roeder ER, Stengel-Rutkowski S, Hennekam RCM, et al (1998) Holoprosencephaly due to mutations in ZIC2, a homologue of Drosophila odd-paired. Nat Genet 20:180–183 - PubMed
-
- Cleveland RH, Holmes LB (1990) Hand-foot-genital syndrome: the importance of hallux varus. Pediatr Radiol 20:339–343 - PubMed
-
- Donnenfeld AE, Schrager DS, Corson SL (1992) Update on a family with hand-foot-genital syndrome: hypospadias and urinary tract abnormalities in two boys from the fourth generation. Am J Med Genet 44:482–484 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

