Hla-DR2-restricted responses to proteolipid protein 95-116 peptide cause autoimmune encephalitis in transgenic mice
- PMID: 10841661
- PMCID: PMC377477
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8407
Hla-DR2-restricted responses to proteolipid protein 95-116 peptide cause autoimmune encephalitis in transgenic mice
Abstract
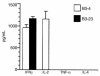
In multiple sclerosis (MS) patients who carry the Class II major histocompatibility (MHC) type HLA-DR2, T cells specific for amino acids 95-116 in the proteolipid protein (PLP) are activated and clonally expanded. However, it remains unclear whether these autoreactive T cells play a pathogenic role or, rather, protect against the central nervous system (CNS) damage. We have addressed this issue, using mice transgenic for the human MHC class II region carrying the HLA-DR2 (DRB1* 1502) haplotype. After stimulating cultured lymph node cells repeatedly with PLP95-116, we generated 2 HLA-DR2-restricted, PLP95-116-specific T-cell lines (TCLs) from the transgenic mice immunized with this portion of PLP. The TCLs were CD4+ and produced T-helper 1 (Th1) cytokines in response to the peptide. These TCLs were adoptively transferred into RAG-2/2 mice expressing HLA-DR2 (DRG1* 1502) molecules. Mice receiving 1 of the TCLs developed a neurological disorder manifested ataxic movement without apparent paresis on day 3, 4, or 5 after cell transfer. Histological examination revealed inflammatory foci primarily restricted to the cerebrum and cerebellum, in association with scattered demyelinating lesions in the deep cerebral cortex. These results support a pathogenic role for PLP95-116-specific T cells in HLA-DR2+ MS patients, and shed light on the possible correlation between autoimmune target epitope and disease phenotype in human CNS autoimmune diseases.
Figures

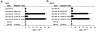
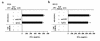


Similar articles
-
A humanized model for multiple sclerosis using HLA-DR2 and a human T-cell receptor.Nat Genet. 1999 Nov;23(3):343-7. doi: 10.1038/15525. Nat Genet. 1999. PMID: 10610182
-
Identification of T cell epitopes on human proteolipid protein and induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in HLA class II-transgenic mice.Eur J Immunol. 2004 Jan;34(1):280-90. doi: 10.1002/eji.200324597. Eur J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14971054
-
Role of MHC class II expressing CD4+ T cells in proteolipid protein(91-110)-induced EAE in HLA-DR3 transgenic mice.Eur J Immunol. 2006 Dec;36(12):3356-70. doi: 10.1002/eji.200636217. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17125142
-
The myelin-associated oligodendrocytic basic protein (MOBP) as a relevant primary target autoantigen in multiple sclerosis.Autoimmun Rev. 2010 Feb;9(4):233-6. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2009.08.002. Epub 2009 Aug 13. Autoimmun Rev. 2010. PMID: 19683076 Review.
-
[T cell immunity to proteolipid protein (PLP) in multiple sclerosis (MS): identification of DR2-associated PLP determinants and conserved TCR CDR3 motifs].Nihon Rinsho. 1994 Nov;52(11):2940-5. Nihon Rinsho. 1994. PMID: 7527867 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
DQB1*0602 rather than DRB1*1501 confers susceptibility to multiple sclerosis-like disease induced by proteolipid protein (PLP).J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Feb 8;9:29. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-29. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22316121 Free PMC article.
-
DQB1*06:02-Associated Pathogenic Anti-Myelin Autoimmunity in Multiple Sclerosis-Like Disease: Potential Function of DQB1*06:02 as a Disease-Predisposing Allele.Front Oncol. 2014 Oct 16;4:280. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00280. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25360418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenic models of autoimmune disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2002 Jan;127(1):4-11. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2002.01771.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11882026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of HLA class II genes in susceptibility and resistance to multiple sclerosis: studies using HLA transgenic mice.J Autoimmun. 2011 Sep;37(2):122-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2011.05.001. Epub 2011 May 31. J Autoimmun. 2011. PMID: 21632210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HLA-transgenic mouse models to study autoimmune central nervous system diseases.Autoimmunity. 2024 Dec;57(1):2387414. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2024.2387414. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Autoimmunity. 2024. PMID: 39167553 Review.
References
-
- Martin R, McFarland HF, McFarlin DE. Immunological aspects of demyelinating diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:153–187. - PubMed
-
- Hafler DA, Weiner HL. Immunologic mechanisms and therapy in multiple sclerosis. Immunol Rev. 1995;144:75–107. - PubMed
-
- Allegretta M, Nicklas JA, Sriram S, Albertini RJ. T cells responsive to myelin basic protein in patients with multiple sclerosis. Science. 1990;247:718–721. - PubMed
-
- Trotter JL, et al. HPRT mutant T-cell lines from multiple sclerosis patients recognize myelin proteolipid peptides. J Neuroimmunol. 1997;75:95–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

