Coreceptor-dependent inhibition of the cell fusion activity of simian immunodeficiency virus Env proteins
- PMID: 10846110
- PMCID: PMC112125
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.13.6217-6222.2000
Coreceptor-dependent inhibition of the cell fusion activity of simian immunodeficiency virus Env proteins
Abstract
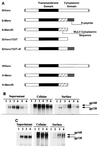
The cytoplasmic tail (R peptide) sequence is able to regulate the fusion activity of the murine leukemia virus (MuLV) envelope (Env) protein. We have previously shown that this sequence exerts a profound inhibitory effect on the fusion activity of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-MuLV chimeric Env proteins which contain the extracellular and transmembrane domains of the SIV Env protein. Recent studies have shown that SIV can utilize several alternative cellular coreceptors for its fusion and entry into the cell. We have investigated the fusion activity of SIV and SIV-MuLV chimeric Env proteins using cells that express different coreceptors. HeLa cells were transfected with plasmid constructs that carry the SIV or SIV-MuLV chimeric Env protein genes and were overlaid with either CEMx174 cells or Ghost Gpr15 cells, which express the Gpr15 coreceptor for SIV, or Ghost CCR5 cells, which express CCR5, an alternate coreceptor for SIV. The R-peptide sequence in the SIV-MuLV chimeric proteins was found to inhibit the fusion with CEMx174 cells or Ghost Gpr15 cells. However, a significant level of fusion was still observed when HeLa cells expressing the chimeric Env proteins were cocultivated with Ghost CCR5 cells. These results show that the R-peptide sequence exerts differential effects on the fusion activity of SIV Env proteins using target cells that express alternative coreceptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amino acid 324 in the simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac V3 loop can confer CD4 independence and modulate the interaction with CCR5 and alternative coreceptors.J Virol. 2004 Apr;78(7):3223-32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.7.3223-3232.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15016843 Free PMC article.
-
Use of GPR1, GPR15, and STRL33 as coreceptors by diverse human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and simian immunodeficiency virus envelope proteins.Virology. 1998 Sep 30;249(2):367-78. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9306. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9791028
-
CXCR6-Mediated Simian Immunodeficiency Virus SIVagmSab Entry into Sabaeus African Green Monkey Lymphocytes Implicates Widespread Use of Non-CCR5 Pathways in Natural Host Infections.J Virol. 2017 Jan 31;91(4):e01626-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01626-16. Print 2017 Feb 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27903799 Free PMC article.
-
The Conformational States of the HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins.Trends Microbiol. 2020 Aug;28(8):655-667. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2020.03.007. Epub 2020 May 14. Trends Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32418859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-function studies of the HIV-1 coreceptors.Semin Immunol. 1998 Jun;10(3):237-48. doi: 10.1006/smim.1998.0130. Semin Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9653050 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein fusion by a membrane-interactive domain in the gp41 cytoplasmic tail.J Virol. 2005 Oct;79(19):12231-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.19.12231-12241.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16160149 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic tail of Moloney murine leukemia virus envelope protein influences the conformation of the extracellular domain: implications for mechanism of action of the R Peptide.J Virol. 2003 Jan;77(2):1281-91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.2.1281-1291.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12502845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1alpha, MIP-1beta receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G, Liao F, Berger E A, Farber J M, Peden K W. A new SIV co-receptor, STRL33. Nature. 1997;388:238. - PubMed
-
- Bron R, Klasse P J, Wilkinson D, Clapham P R, Pelchen-Matthews A, Power C, Wells T N C, Kim J, Peiper S C, Hoxie J A, Marsh M. Promiscuous use of CC and CXC chemokine receptors in cell-to-cell fusion mediated by a human immunodeficiency virus type 2 envelope protein. J Virol. 1997;71:8405–8415. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bullough P A, Hughson F M, Skehel J J, Wiley D C. Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature. 1994;371:37–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

