Phosphorylated PmrA interacts with the promoter region of ugd in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
- PMID: 10851011
- PMCID: PMC94567
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.13.3874-3876.2000
Phosphorylated PmrA interacts with the promoter region of ugd in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
Abstract
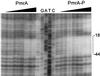
The Salmonella PmrA-PmrB system controls the expression of genes necessary for polymyxin B resistance. Four loci were previously identified as part of the regulon, and interaction of PmrA with the promoter region of three of them was observed. Here we characterized the interaction of PmrA with the promoter region of ugd, previously suggested to be regulated indirectly by PmrA. Our results indicate that PmrA controls the expression of ugd by interacting with a specific sequence in the promoter region of this gene.
Figures


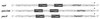
References
-
- Baker S J, Gunn J S, Morona R. The Salmonella typhi melittin resistance gene pqaB affects intracellular growth in PMA-differentiated U937 cells, polymyxin B resistance and lipopolysaccharide. Microbiology. 1999;145:367–378. - PubMed
-
- Cullen P J, Bowman W C, Kranz R G. In vitro reconstitution and characterization of the Rhodobacter capsulatus NtrB and NtrC two-component system. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:6530–6536. - PubMed
-
- Dougherty B A, van de Rijn I. Molecular characterization of hasB from an operon required for hyaluronic acid synthesis in group A streptococci. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:7118–7124. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

