The tyrosine kinase PYK-2/RAFTK regulates natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxic response, and is translocated and activated upon specific target cell recognition and killing
- PMID: 10851022
- PMCID: PMC2175114
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.6.1249
The tyrosine kinase PYK-2/RAFTK regulates natural killer (NK) cell cytotoxic response, and is translocated and activated upon specific target cell recognition and killing
Abstract
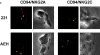
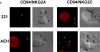
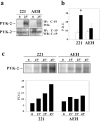
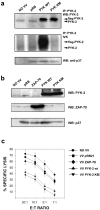
The compartmentalization of plasma membrane proteins has a key role in regulation of lymphocyte activation and development of immunity. We found that the proline-rich tyrosine kinase-2 (PYK-2/RAFTK) colocalized with the microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) at the trailing edge of migrating natural killer (NK) cells. When polyclonal NK cells bound to K562 targets, PYK-2 translocated to the area of NK-target cell interaction. The specificity of this process was assessed with NK cell clones bearing activatory or inhibitory forms of CD94/NKG2. The translocation of PYK-2, MTOC, and paxillin to the area of NK-target cell contact was regulated upon specific recognition of target cells through NK cell receptors, controlling target cell killing. Furthermore, parallel in vitro kinase assays showed that PYK-2 was activated in response to signals that specifically triggered its translocation and NK cell mediated cytotoxicity. The overexpression of both the wt and a dominant-negative mutant of PYK-2, but not ZAP-70 wt, prevented the specific translocation of the MTOC and paxillin, and blocked the cytotoxic response of NK cells. Our data indicate that subcellular compartmentalization of PYK-2 correlates with effective signal transduction. Furthermore, they also suggest an important role for PYK-2 on the assembly of the signaling complexes that regulate the cytotoxic response.
Figures






References
-
- Aramburu J., Balboa M.A., Ramírez A., Silva A., Acevedo A., Sánchez-Madrid F., de Landázuri M.O., López-Botet M. A novel functional cell surface dimer (Kp43) expressed by natural killer cells and T cell receptor-γδ T lymphocytes. Inhibition of IL-2 dependent proliferation by anti-Kp43 monoclonal antibody. J. Immunol. 1990;147:714–721. - PubMed
-
- Astier A., Avraham H., Manie S.N., Groopman J., Canty T., Avraham S., Freedman A.S. The related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase is tyrosine phosphorylated after β1-integrin stimulation in B cells and binds to p130cas . J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Avraham S., London R., Fu Y., Ota S., Hiregowdara D., Li S., Jiang S., Pasztor L.M., White R.A., Groopman J.E., Avraham H. Identification and characterization of a novel related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase (RAFTK) from megakaryocytes and brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:27742–27751. - PubMed
-
- Berg N.N., Ostergaard H.L. T cell receptor engagement induces tyrosine phosphorylation of FAK and PYK-2 and their association with Lck. J. Immunol. 1997;159:1753–1757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

