Point mutations in a peptidoglycan biosynthesis gene cause competence induction in Haemophilus influenzae
- PMID: 10852860
- PMCID: PMC101876
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.12.3323-3330.2000
Point mutations in a peptidoglycan biosynthesis gene cause competence induction in Haemophilus influenzae
Abstract
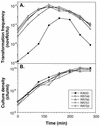
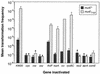
We have identified three new Haemophilus influenzae mutations causing cells to exhibit extreme hypercompetence at all stages of growth. The mutations are in murE, which encodes the meso-diaminopimelate-adding enzyme of peptidoglycan synthesis. All are point mutations causing nonconservative amino acid substitutions, two at a poorly conserved residue (G(435)-->R and G(435)-->W) and the third at a highly conserved leucine (L(361)-->S). The mutant strains have very similar phenotypes and do not exhibit any defects in cell growth, permeability, or sensitivity to peptidoglycan antibiotics. Cells retain the normal specificity of DNA uptake for the H. influenzae uptake signal sequence. The mutations do not bypass genes known to be needed for competence induction but do dramatically increase expression of genes required for the normal pathway of DNA uptake. We conclude that the mutations do not act by increasing cell permeability but by causing induction of the normal competence pathway via a previously unsuspected signal.
Figures


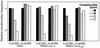

Similar articles
-
Biochemical characterization of UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate: meso-2,6-diaminopimelate ligase (MurE) from Verrucomicrobium spinosum DSM 4136(T.).PLoS One. 2013 Jun 13;8(6):e66458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066458. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23785498 Free PMC article.
-
Structural organization, nucleotide sequence, and regulation of the Haemophilus influenzae rec-1+ gene.J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7269-81. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7269-7281.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8226674 Free PMC article.
-
The Haemophilus influenzae adenylate cyclase gene: cloning, sequence, and essential role in competence.J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(22):7142-9. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.22.7142-7149.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8226661 Free PMC article.
-
RNA secondary structure regulates the translation of sxy and competence development in Haemophilus influenzae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(1):10-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm915. Epub 2007 Nov 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 17981840 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of antimicrobial resistance in non-typable Haemophilus influenzae.Microbiologia. 1997 Sep;13(3):309-14. Microbiologia. 1997. PMID: 9353749 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial Transformation Buffers Environmental Fluctuations through the Reversible Integration of Mobile Genetic Elements.mBio. 2020 Mar 3;11(2):e02443-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02443-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32127449 Free PMC article.
-
The availability of purine nucleotides regulates natural competence by controlling translation of the competence activator Sxy.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Jun;88(6):1106-19. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12245. Epub 2013 May 13. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23663205 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hypercompetence in Legionella pneumophila.J Bacteriol. 2004 Jun;186(12):3814-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.12.3814-3825.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15175295 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple interspecies recombination events documented by whole-genome sequencing in multidrug-resistant Haemophilus influenzae clinical isolates.Access Microbiol. 2024 Feb 12;6(2):000649.v3. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000649.v3. eCollection 2024. Access Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38482359 Free PMC article.
-
tfoX (sxy)-dependent transformation of Aggregatibacter (Actinobacillus) actinomycetemcomitans.Gene. 2007 Sep 1;399(1):53-64. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.04.026. Epub 2007 May 1. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17561357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister L A. An RNA secondary structure regulates sxy expression and competence development in Haemophilus influenzae. Ph.D. Thesis. Vancouver, Canada: University of British Columbia; 1999.
-
- Barcak G J, Chandler M S, Redfield R J, Tomb J-F. Genetic systems in Haemophilus influenzae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:321–342. - PubMed
-
- Bouhss A, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Blanot D, van Heijenoort J, Parquet C. Invariant amino acids in the Mur peptide synthetases of bacterial peptidoglycan synthesis and their modification by site-directed mutagenesis in the UDP-MurNAc:L-alanine ligase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1997;36:11556–11563. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

