In Lactobacillus plantarum, carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized by two carbamoyl-phosphate synthetases (CPS): carbon dioxide differentiates the arginine-repressed from the pyrimidine-regulated CPS
- PMID: 10852872
- PMCID: PMC101912
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.12.3416-3422.2000
In Lactobacillus plantarum, carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized by two carbamoyl-phosphate synthetases (CPS): carbon dioxide differentiates the arginine-repressed from the pyrimidine-regulated CPS
Abstract
Carbamoyl phosphate (CP) is an intermediate in pyrimidine and arginine biosynthesis. Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (CPS) contains a small amidotransferase subunit (GLN) that hydrolyzes glutamine and transfers ammonia to the large synthetase subunit (SYN), where CP biosynthesis occurs in the presence of ATP and CO(2). Lactobacillus plantarum, a lactic acid bacterium, harbors a pyrimidine-inhibited CPS (CPS-P; Elagöz et al., Gene 182:37-43, 1996) and an arginine-repressed CPS (CPS-A). Sequencing has shown that CPS-A is encoded by carA (GLN) and carB (SYN). Transcriptional studies have demonstrated that carB is transcribed both monocistronically and in the carAB arginine-repressed operon. CP biosynthesis in L. plantarum was studied with three mutants (DeltaCPS-P, DeltaCPS-A, and double deletion). In the absence of both CPSs, auxotrophy for pyrimidines and arginine was observed. CPS-P produced enough CP for both pathways. In CO(2)-enriched air but not in ordinary air, CPS-A provided CP only for arginine biosynthesis. Therefore, the uracil sensitivity observed in prototrophic wild-type L. plantarum without CO(2) enrichment may be due to the low affinity of CPS-A for its substrate CO(2) or to regulation of the CP pool by the cellular CO(2)/bicarbonate level.
Figures


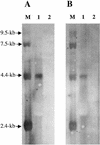
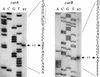
References
-
- Bringel F. Carbamoylphosphate and natural auxotrophies in lactic acid bacteria. Lait. 1998;78:31–37.
-
- Delannay S, Charlier D, Tricot C, Villeret V, Piérard A, Stalon V. Serine 948 and threonine 1042 are crucial residues for allosteric regulation of Escherichia coli carbamoylphosphate synthetase and illustrate coupling effects of activation and inhibition pathways. J Mol Biol. 1999;286:1217–1228. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

