Roles of cyclic AMP receptor protein and the carboxyl-terminal domain of the alpha subunit in transcription activation of the Escherichia coli rhaBAD operon
- PMID: 10852886
- PMCID: PMC101950
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.12.3529-3535.2000
Roles of cyclic AMP receptor protein and the carboxyl-terminal domain of the alpha subunit in transcription activation of the Escherichia coli rhaBAD operon
Abstract
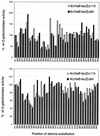
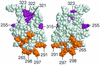
The Escherichia coli rhaBAD operon encodes the enzymes for catabolism of the sugar L-rhamnose. Full rhaBAD activation requires the AraC family activator RhaS (bound to a site that overlaps the -35 region of the promoter) and the cyclic AMP receptor protein (CRP; bound immediately upstream of RhaS at -92.5). We tested alanine substitutions in activating regions (AR) 1 and 2 of CRP for their effect on rhaBAD activation. Some, but not all, of the substitutions in both AR1 and AR2 resulted in approximately twofold defects in expression from rhaBAD promoter fusions. We also expressed a derivative of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase deleted for the entire C-terminal domain (alpha-Delta235) and assayed expression from rhaBAD promoter fusions. The greatest defect (54-fold) occurred at a truncated promoter where RhaS was the only activator, while the defect at the full-length promoter (RhaS plus CRP) was smaller (13-fold). Analysis of a plasmid library expressing alanine substitutions at every residue in the carboxyl-terminal domain of the alpha subunit (alpha-CTD) identified 15 residues (mostly in the DNA-binding determinant) that were important at both the full-length and truncated promoters. Only one substitution was defective at the full-length but not the truncated promoter, and this residue was located in the DNA-binding determinant. Six substitutions were defective only at the promoter activated by RhaS alone, and these may define a protein-contacting determinant on alpha-CTD. Overall, our results suggest that CRP interaction with alpha-CTD may not be required for rhaBAD activation; however, alpha-CTD does contribute to full activation, probably through interactions with DNA and possibly RhaS.
Figures

References
-
- Blatter E E, Ross W, Tang H, Gourse R L, Ebright R H. Domain organization of RNA polymerase α subunit: C-terminal 85 amino acids constitute a domain capable of dimerization and DNA binding. Cell. 1994;78:889–896. - PubMed
-
- Busby S, Ebright R H. Transcription activation at class II CAP-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1997;23:853–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

