Megaplasmid pRme2011a of Sinorhizobium meliloti is not required for viability
- PMID: 10852892
- PMCID: PMC101967
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.182.12.3582-3586.2000
Megaplasmid pRme2011a of Sinorhizobium meliloti is not required for viability
Abstract
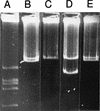
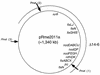
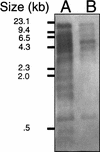
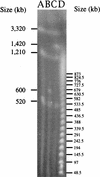
We report the curing of the 1,360-kb megaplasmid pRme2011a from Sinorhizobium meliloti strain Rm2011. With a positive selection strategy that utilized Tn5B12-S containing the sacB gene, we were able to cure this replicon by successive rounds of selecting for deletion formation in vivo. Subsequent Southern blot, Eckhardt gel, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analyses were consistent with the hypothesis that the resultant strain was indeed missing pRme2011a. The cured derivative grew as well as the wild-type strain in both complex and defined media but was unable to use a number of substrates as a sole source of carbon on defined media.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteome analysis demonstrates complex replicon and luteolin interactions in pSyma-cured derivatives of Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 2011.Electrophoresis. 2000 Nov;21(17):3833-42. doi: 10.1002/1522-2683(200011)21:17<3833::AID-ELPS3833>3.0.CO;2-I. Electrophoresis. 2000. PMID: 11271501
-
Sequence analysis of the 181-kb accessory plasmid pSmeSM11b, isolated from a dominant Sinorhizobium meliloti strain identified during a long-term field release experiment.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 Jun;271(2):297-309. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00731.x. Epub 2007 Apr 27. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17466030
-
The tRNAarg gene and engA are essential genes on the 1.7-Mb pSymB megaplasmid of Sinorhizobium meliloti and were translocated together from the chromosome in an ancestral strain.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jan;195(2):202-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.01758-12. Epub 2012 Nov 2. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23123907 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution physical map of the pSymb megaplasmid and comparison of the three replicons of Sinorhizobium meliloti strain 1021.Curr Microbiol. 2000 Aug;41(2):109-13. doi: 10.1007/s002840010103. Curr Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10856376
-
High-resolution physical map of the Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 pSyma megaplasmid.J Bacteriol. 2000 Feb;182(4):1185-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.4.1185-1189.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10648551 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Large-scale genetic variation of the symbiosis-required megaplasmid pSymA revealed by comparative genomic analysis of Sinorhizobium meliloti natural strains.BMC Genomics. 2005 Nov 10;6:158. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-6-158. BMC Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16283928 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum sensing in nitrogen-fixing rhizobia.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003 Dec;67(4):574-92. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.4.574-592.2003. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003. PMID: 14665677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleotide sequence and predicted functions of the entire Sinorhizobium meliloti pSymA megaplasmid.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Aug 14;98(17):9883-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.161294798. Epub 2001 Jul 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11481432 Free PMC article.
-
pSymA-dependent mobilization of the Sinorhizobium meliloti pSymB megaplasmid.J Bacteriol. 2010 Dec;192(23):6309-12. doi: 10.1128/JB.00549-10. Epub 2010 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20889746 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling of a Sinorhizobium meliloti fadD mutant reveals the role of rhizobactin 1021 biosynthesis and regulation genes in the control of swarming.BMC Genomics. 2010 Mar 8;11:157. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-157. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20210991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banfalvi Z, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A. Rhizobium meliloti carries two megaplasmids. Plasmid. 1985;13:129–138. - PubMed
-
- Banfalvi Z, Sakanyan V, Koncz C, Kiss A, Dusha I, Kondorosi A. Location of nitrogen fixation genes on a high molecular weight plasmid of R. meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184:318–325. - PubMed
-
- Barnett M J, Long S R. Identification and characterization of a gene on Rhizobium meliloti pSyma, syrB, that negatively affects syrM expression. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 1997;10:550–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

