Repression of shoot growth, a bZIP transcriptional activator, regulates cell elongation by controlling the level of gibberellins
- PMID: 10852936
- PMCID: PMC149092
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.6.901
Repression of shoot growth, a bZIP transcriptional activator, regulates cell elongation by controlling the level of gibberellins
Abstract
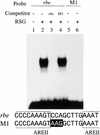
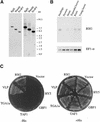
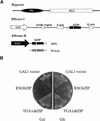
Cell expansion, a developmental process regulated by both endogenous programs and environmental stimuli, is critically important for plant growth. Here, we report the isolation and characterization of RSG (for repression of shoot growth), a transcriptional activator with a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domain. To examine the role of RSG in plant development, we generated transgenic tobacco plants expressing a dominant-negative form of RSG, which repressed the activity of full-length RSG. In transgenic plants, this expression severely inhibited stem internode growth, specifically cell elongation. These plants also had less endogenous amounts of the major active gibberellin (GA) in tobacco, GA(1). Applying GAs restored the dwarf phenotypes of transgenic tobacco plants that expressed the dominant-negative form of RSG. To investigate the function of RSG in the regulation of the endogenous amounts of GAs, we identified a target for RSG. RSG bound and activated the promoter of Arabidopsis GA3, one of the genes encoding enzymes involved in GA biosynthesis. Moreover, the dominant-negative form of RSG decreased expression of the GA3 homolog in transgenic tobacco plants. Our results show that RSG, a bZIP transcriptional activator, regulates the morphology of plants by controlling the endogenous amounts of GAs.
Figures







References
-
- Aeschbacher, R.A., Schrott, M., Potrykas, I., and Saul, M.W. (1991). Isolation and molecular characterization of PosF21, an Arabidopsis thaliana gene which shows characteristics of a bZIP class transcription factor. Plant J. 1, 303–316. - PubMed
-
- Aukerman, M.J., Schmidt, R.J., Burr, B., and Burr, F.A. (1991). An arginine to lysine substitution in the bZIP domain of an opaque2 mutant in maize abolishes specific DNA binding. Genes Dev. 5, 310–320. - PubMed
-
- Baluška, F., Parker, J.S., and Barlow, P.W. (1993). A role for gibberellic acid in orienting microtubules and regulating cell growth polarity in the maize root cortex. Planta 191, 149–157.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

