St. John's wort induces hepatic drug metabolism through activation of the pregnane X receptor
- PMID: 10852961
- PMCID: PMC16574
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.130155097
St. John's wort induces hepatic drug metabolism through activation of the pregnane X receptor
Abstract
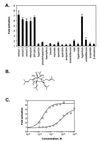
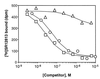
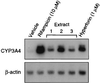
St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) is an herbal remedy used widely for the treatment of depression. Recent clinical studies demonstrate that hypericum extracts increase the metabolism of various drugs, including combined oral contraceptives, cyclosporin, and indinavir. In this report, we show that hyperforin, a constituent of St. John's wort with antidepressant activity, is a potent ligand (K(i) = 27 nM) for the pregnane X receptor, an orphan nuclear receptor that regulates expression of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 monooxygenase. Treatment of primary human hepatocytes with hypericum extracts or hyperforin results in a marked induction of CYP3A4 expression. Because CYP3A4 is involved in the oxidative metabolism of >50% of all drugs, our findings provide a molecular mechanism for the interaction of St. John's wort with drugs and suggest that hypericum extracts are likely to interact with many more drugs than previously had been realized.
Figures
Similar articles
-
St John's wort, a herbal antidepressant, activates the steroid X receptor.J Endocrinol. 2000 Sep;166(3):R11-6. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.166r011. J Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10974665
-
Effect of the St. John's wort constituent hyperforin on docetaxel metabolism by human hepatocyte cultures.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Oct 1;11(19 Pt 1):6972-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-2488. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16203790
-
Variability in PXR-mediated induction of CYP3A4 by commercial preparations and dry extracts of St. John's wort.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2007 Aug;375(6):377-82. doi: 10.1007/s00210-007-0172-8. Epub 2007 Jun 26. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17593354
-
Hyperforin in St. John's wort drug interactions.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Mar;62(3):225-33. doi: 10.1007/s00228-006-0096-0. Epub 2006 Feb 14. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16477470 Review.
-
Usefulness of studies on the molecular mechanism of action of herbals/botanicals: The case of St. John's wort.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2005;19(1):1-11. doi: 10.1002/jbt.20057. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15736155 Review.
Cited by
-
Ophiopogon japonicus strains from different cultivation regions exhibit markedly different properties on cytotoxicity, pregnane X receptor activation and cytochrome P450 3A4 induction.Biomed Rep. 2015 May;3(3):430-434. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.443. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Biomed Rep. 2015. PMID: 26137250 Free PMC article.
-
Sesamin: A Naturally Occurring Lignan Inhibits CYP3A4 by Antagonizing the Pregnane X Receptor Activation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:242810. doi: 10.1155/2012/242810. Epub 2012 May 7. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22645625 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer chemoprevention by carotenoids.Molecules. 2012 Mar 14;17(3):3202-42. doi: 10.3390/molecules17033202. Molecules. 2012. PMID: 22418926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological perspectives on the detoxification of plant secondary metabolites: implications for ingestive behavior of herbivores.J Chem Ecol. 2006 Jun;32(6):1213-28. doi: 10.1007/s10886-006-9081-4. Epub 2006 May 23. J Chem Ecol. 2006. PMID: 16770714 Review.
-
Drug interaction between St John's Wort and quazepam.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004 Oct;58(4):403-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02171.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15373933 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Volz H P. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1997;2:72–76. - PubMed
-
- Wheatley D. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1997;2:77–80. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya S K, Chakrabarti A, Chatterjee S S. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1998;1:22–29. - PubMed
-
- Butterweck V, Wall A, Lieflander-Wulf U, Winterhoff H, Nahrstedt A. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1997;2:117–124. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

