Precise gene localization by phenotypic assay of radiation hybrid cells
- PMID: 10852967
- PMCID: PMC16555
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.130200097
Precise gene localization by phenotypic assay of radiation hybrid cells
Abstract
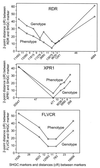
A high resolution map of the human genome previously has been constructed by using the G3 panel of human/hamster radiation hybrid cell lines and >15,000 unique human genetic markers. By determining whether human DNA sequences are present or absent in each of the hybrids, localization of single genes may routinely be achieved at approximately 250-kb resolution. In this paper we have tested whether similarly precise localization might be achieved by phenotypic screening of the hybrids to facilitate positional cloning of unknown genes. We assayed the susceptibility of each of the hybrid cell lines to transduction by retroviral vectors bearing different retroviral envelope proteins that recognize receptors present on human but not on hamster cells. The results for each of the retroviral vectors were informative and allowed precise localization of the receptor genes for the RD114 cat endogenous retrovirus, xenotropic murine leukemia virus, and type C feline leukemia virus. After cloning of the receptors for these retroviruses, we found that standard genotypic mapping by PCR gave results that were nearly identical to those from phenotypic mapping. These experiments show that precise gene localization by phenotypic assay of radiation hybrids is practical and was not appreciably impacted by the known instability of such hybrid cells. This technique should be applicable to many other human genes having discernible phenotypes in hamster cells and, with completion of the human genome project, will allow rapid identification of unknown genes on the basis of phenotype.
Figures
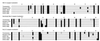

References
-
- Stewart E A, McKusick K B, Aggarwal A, Bajorek E, Brady S, Chu A, Fang N, Hadley D, Harris M, Hussain S, et al. Genome Res. 1997;7:422–433. - PubMed
-
- Goss S J, Harris H. Nature (London) 1975;255:680–684. - PubMed
-
- Hunter E. In: Retroviruses. Coffin J M, Hughes S H, Varmus H E, editors. Plainview, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press; 1997. pp. 71–119.
-
- Weiss R A. In: The Retroviridae. Levy J A, editor. Vol. 2. New York: Plenum; 1993. pp. 1–108.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

