Expression of the integrin alpha8beta1 during pulmonary and hepatic fibrosis
- PMID: 10854216
- PMCID: PMC1850077
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65066-3
Expression of the integrin alpha8beta1 during pulmonary and hepatic fibrosis
Abstract
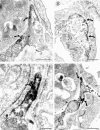
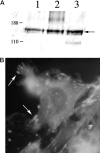
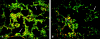
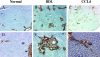
The fibrotic response after diverse forms of injury is characterized by the accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins, proliferation of myofibroblast-like cells, and organ contraction. Myofibroblasts are key effector cells in the development of the fibrotic response. They contribute to fibrosis through both increased cell number (proliferation) and enhanced matrix synthesis. Integrins, a class of cell adhesion molecules, are mediators of cell-extracellular matrix protein interactions that are important in the proliferative and migratory response of cells to matrix proteins. We have previously cloned the human integrin subunit alpha8, documented its high expression in lung tissue, and established it as a receptor for the matrix proteins fibronectin, vitronectin, and tenascin. We now demonstrate that alveolar interstitial cells are the primary cell type expressing alpha8beta1 in the lung parenchyma. Expression of alpha8beta1 is concentrated primarily along the thinned extensions of cells and at the tips of filopodia. Because of its unique distribution in alveolar interstitial cells, we hypothesized that it may play a role in the fibrotic response after injury. In bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis, there is increased expression of alpha8beta1 by interstitial fibroblasts, the majority of which coexpress alpha smooth muscle actin, a marker of tissue myofibroblasts. To establish a more general role for alpha8beta1 during organ fibrosis, we further examined its expression in two rat models of liver fibrosis. During hepatic injury due to either carbon tetrachloride injury or bile duct ligation, we demonstrate de novo expression of alpha8beta1 in activated hepatic stellate cells, the myofibroblast equivalent in liver. Taken together, the data localize alpha8beta1 to myofibroblast-like cells during wound healing and suggest that signal transduction through the alpha8beta1 integrin may contribute to the fibrotic response of organs to injury.
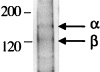
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alpha8beta1 integrin is upregulated in myofibroblasts of fibrotic and scarring myocardium.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004 Mar;36(3):343-53. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2003.11.007. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15010273
-
Induced hepatic stellate cell integrin, α8β1, enhances cellular contractility and TGFβ activity in liver fibrosis.J Pathol. 2021 Apr;253(4):366-373. doi: 10.1002/path.5618. Epub 2021 Feb 19. J Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33433924 Free PMC article.
-
Fibronectin extra domain-A promotes hepatic stellate cell motility but not differentiation into myofibroblasts.Gastroenterology. 2012 Apr;142(4):928-937.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.038. Epub 2011 Dec 24. Gastroenterology. 2012. PMID: 22202457 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases, hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998 Sep;13 Suppl:S33-8. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1998. PMID: 9792032 Review.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in fibrosis and repair. Transforming growth factor-β activation by epithelial cells and fibroblasts.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015 Mar;12 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S21-3. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201406-245MG. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015. PMID: 25830829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of an interleukin 13-induced epigenetic signature in allergic airway inflammation.Am J Transl Res. 2012;4(2):219-28. Epub 2012 Apr 10. Am J Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 22611474 Free PMC article.
-
Fra-2 negatively regulates postnatal alveolar septation by modulating myofibroblast function.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;313(5):L878-L888. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00062.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28818870 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins and heparan sulfate proteoglycans on hepatic stellate cells (HSC) are novel receptors for HSC-derived exosomes.FEBS Lett. 2016 Dec;590(23):4263-4274. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12448. Epub 2016 Oct 23. FEBS Lett. 2016. PMID: 27714787 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrosis: cross-organ biology and pathways to development of innovative drugs.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025 Jul;24(7):543-569. doi: 10.1038/s41573-025-01158-9. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 40102636 Review.
-
The Development of Integrin Alpha-8 Deficient Lungs Shows Reduced and Altered Branching and a Correction of the Phenotype During Alveolarization.Front Physiol. 2020 Dec 21;11:530635. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.530635. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33408636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kapanci Y, Costabella PM, Cerutti P, Assimacopoulos A: Distribution and function of cytoskeletal proteins in lung cells with particular reference to “contractile interstitial cells.” Methods Achiev Exp Pathol 1979, 9:147-168 - PubMed
-
- Fukui M, Yasui H, Watanabe K, Fujimoto T, Kakuma T, Yoshida R, Ohi M, Kuno K: Hypoxic contraction of contractile interstitial cells isolated from bovine lung. Am J Physiol 1996, 270:L962-L972 - PubMed
-
- Weibel ER, Crystal RG: Structural organization of the pulmonary interstitium. Crystal RG West JB eds. The Lung: Scientific Foundations, 1991, vol 1.:pp 369-380 Raven Press, New York
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

