Adenosine A1 receptors modulate high voltage-activated Ca2+ currents and motor pattern generation in the xenopus embryo
- PMID: 10856119
- PMCID: PMC2269976
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00655.x
Adenosine A1 receptors modulate high voltage-activated Ca2+ currents and motor pattern generation in the xenopus embryo
Abstract
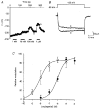
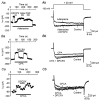
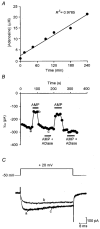
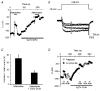
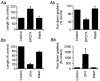
Adenosine causes voltage- and non-voltage-dependent inhibition of high voltage-activated (HVA) Ca2+ currents in Xenopus laevis embryo spinal neurons. As this inhibition can be blocked by 8-cyclopentyl-1, 3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX) and mimicked by N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) it appears to be mediated by A1 receptors. Agents active at A2 receptors either were without effect or could be blocked by DPCPX. AMP had no agonist action on these receptors. By using omega-conotoxin GVIA we found that adenosine inhibited an N-type Ca2+ current as well as a further unidentified HVA current that was insensitive to dihydropyridines, omega-agatoxin TK and omega-conotoxin MVIIC. Both types of current were subject to voltage- and non-voltage-dependent inhibition. We used CPA and DPCPX to test whether A1 receptors regulated spinal motor pattern generation in spinalized Xenopus embryos. DPCPX caused a near doubling of, while CPA greatly shortened, the length of swimming episodes. In addition, DPCPX slowed, while CPA greatly speeded up, the rate of run-down of motor activity. Our results demonstrate a novel action of A1 receptors in modulating spinal motor activity. Furthermore they confirm that adenosine is produced continually throughout swimming episodes and acts to cause the eventual termination of activity.
Figures


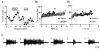
References
-
- Agarwhal RP, Parks RE. Adenosine deaminase from human erythrocytes. Methods in Enzymology. 1978;51:502–507. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosio AF, Malva JO, Carvalho AP, Carvalho CM. Modulation of Ca2+ channels by activation of adenosine A1 receptors in rat striatal glutamatergic nerve terminals. Neuroscience Letters. 1996;220:163–166. - PubMed
-
- Ambrosio AF, Malva JO, Carvalho AP, Carvalho CM. Inhibition of N- and P/Q- and other types of Ca2+ channel in rat hippocampal nerve terminals by the adenosine A1 receptor. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1997;340:301–310. - PubMed
-
- Burnstock G, Wood JN. Purinergic receptors – their role in nociception and primary afferent neurotransmission. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 1996;6:526–532. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Van Den Pol AN. Adenosine modulation of calcium currents and presynaptic inhibition of GABA release in suprachiasmatic and arcuate nucleus neurones. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1997;77:3035–3047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

