Congenital hereditary lymphedema caused by a mutation that inactivates VEGFR3 tyrosine kinase
- PMID: 10856194
- PMCID: PMC1287178
- DOI: 10.1086/303019
Congenital hereditary lymphedema caused by a mutation that inactivates VEGFR3 tyrosine kinase
Abstract
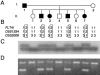
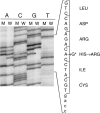
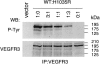
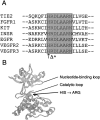
Hereditary lymphedema is a chronic swelling of limbs due to dysfunction of lymphatic vessels. An autosomal dominant, congenital form of the disease, also known as "Milroy disease," has been mapped to the telomeric part of chromosome 5q, in the region 5q34-q35. This region contains a good candidate gene for the disease, VEGFR3 (FLT4), that encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase specific for lymphatic vessels. To clarify the role of VEGFR3 in the etiology of the disease, we have analyzed a family with hereditary lymphedema. We show linkage of the disease with markers in 5q34-q35, including a VEGFR3 intragenic polymorphism, and we describe an A-->G transition that cosegregates with the disease, corresponding to a histidine-to-arginine substitution in the catalytic loop of the protein. In addition, we show, by in vitro expression, that this mutation inhibits the autophosphorylation of the receptor. Thus, defective VEGFR3 signaling seems to be the cause of congenital hereditary lymphedema linked to 5q34-q35.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/index.html (for accession numbers X68203 for VEGFR3 short form and S66407 for c-terminal tail of VEGFR3 long form)
-
- SwissProt, http://www.expasy.ch/sprot/ (for VEGFR3, accession number P35916)
References
-
- Boon LM, Mulliken JB, Vikkula M, Watkins H, Seidman J, Olsen BR, Warman ML (1994) Assignment of a locus for dominantly inherited venous malformations to chromosome 9p. Hum Mol Genet 3:1583–1587 - PubMed
-
- Dumont DJ, Jussila L, Taipale J, Lymboussaki A, Mustonen T, Pajusola K, Breitman M, et al (1998) Cardiovascular failure in mouse embryos deficient in VEGF receptor-3. Science 282:946–949 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

