Granulocytic ehrlichiosis in mice deficient in phagocyte oxidase or inducible nitric oxide synthase
- PMID: 10858261
- PMCID: PMC101771
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.7.4361-4362.2000
Granulocytic ehrlichiosis in mice deficient in phagocyte oxidase or inducible nitric oxide synthase
Abstract
Mice deficient in phox (gp91(phox-/-)) or NOS2 (NOS2(-/-)) were infected with the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis (HGE) to evaluate the importance of these pathways in the eradication of HGE bacteria. NOS2(-/-) mice had delayed clearance of the HGE agent in comparison to control or gp91(phox-/-) mice, suggesting that reactive nitrogen intermediates play a role in the early control of HGE.
Figures
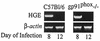

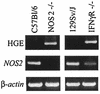
References
-
- Banerjee R, Anguita J, Roos D, Fikrig E. Infection by the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis prevents the respiratory burst by downregulating gp91phox. J Immunol. 2000;164:3946–3949. - PubMed
-
- Bunnell J E, Trigiani E R, Srinivas S R, Dumler J S. Development and distribution of pathologic lesions are related to immune status and tissue deposition of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis agent-infected cells in a murine model system. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:546–550. - PubMed
-
- Christova I S, Dumler J S. Human granulocytic ehrlichiosis in Bulgaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1999;60:58–61. - PubMed
-
- Dinauer M C, Deck M B, Unanue E R. Mice lacking reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activity show increased susceptibility to early infection with Listeria monocytogenes. J Immunol. 1997;158:5581–5583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

