Stenotrophomonas maltophilia D457R contains a cluster of genes from gram-positive bacteria involved in antibiotic and heavy metal resistance
- PMID: 10858330
- PMCID: PMC89961
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.7.1778-1782.2000
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia D457R contains a cluster of genes from gram-positive bacteria involved in antibiotic and heavy metal resistance
Abstract
A cluster of genes involved in antibiotic and heavy metal resistance has been characterized from a clinical isolate of the gram-negative bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. These genes include a macrolide phosphotransferase (mphBM) and a cadmium efflux determinant (cadA), together with the gene cadC coding for its transcriptional regulator. The cadC cadA region is flanked by a truncated IS257 sequence and a region coding for a bin3 invertase. Despite their presence in a gram-negative bacterium, these genetic elements share a common gram-positive origin. The possible origin of these determinants as a remnant composite transposon as well as the role of gene transfer between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria for the acquisition of antibiotic resistance determinants in chronic, mixed infections is discussed.
Figures
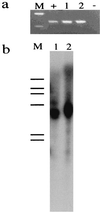
References
-
- Arpi M, Victor M A, Mortensen I, Gottschau A, Bruun B. In vitro susceptibility of 124 Xanthomonas maltophilia (Stenotrophomonas maltophilia) isolates: comparison of the agar dilution method with the E-test and two agar diffusion methods. APMIS. 1996;104:108–114. - PubMed
-
- Atlas R M. Handbook of microbiological media. London, England: CRC Press, Inc.; 1993.
-
- Bagdasarian M, Bagdasarian M M. Gene cloning and expression. In: Gerhardt P, Murray R G E, Wood W A, Krieg N R, editors. Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. Washington, D.C.: American Society for Microbiology; 1994. pp. 406–417.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

