Quinupristin-dalfopristin combined with beta-lactams for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus constitutively resistant to macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics
- PMID: 10858332
- PMCID: PMC89963
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.7.1789-1795.2000
Quinupristin-dalfopristin combined with beta-lactams for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to Staphylococcus aureus constitutively resistant to macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B antibiotics
Abstract
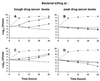
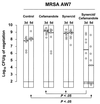
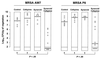
Quinupristin-dalfopristin (Q-D) is an injectable streptogramin active against most gram-positive pathogens, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In experimental endocarditis, however, Q-D was less efficacious against MRSA isolates constitutively resistant to macrolide-lincosamide-streptogram B (C-MLS(B)) than against MLS(B)-susceptible isolates. To circumvent this problem, we used the checkerboard method to screen drug combinations that would increase the efficacy of Q-D against such bacteria. beta-Lactams consistently exhibited additive or synergistic activity with Q-D. Glycopeptides, quinolones, and aminoglycosides were indifferent. No drugs were antagonistic. The positive Q-D-beta-lactam interaction was independent of MLS(B) or beta-lactam resistance. Moreover, addition of Q-D at one-fourth the MIC to flucloxacillin-containing plates decreased the flucloxacillin MIC for MRSA from 500 to 1,000 mg/liter to 30 to 60 mg/liter. Yet, Q-D-beta-lactam combinations were not synergistic in bactericidal tests. Rats with aortic vegetations were infected with two C-MLS(B)-resistant MRSA isolates (isolates AW7 and P8) and were treated for 3 or 5 days with drug dosages simulating the following treatments in humans: (i) Q-D at 7 mg/kg two times a day (b.i.d.) (a relatively low dosage purposely used to help detect positive drug interactions), (ii) cefamandole at constant levels in serum of 30 mg/liter, (iii) cefepime at 2 g b.i.d., (iv) Q-D combined with either cefamandole or cefepime. Any of the drugs used alone resulted in treatment failure. In contrast, Q-D plus either cefamandole or cefepime significantly decreased valve infection compared to the levels of infection for both untreated controls and those that received monotherapy (P < 0.05). Importantly, Q-D prevented the growth of highly beta-lactam-resistant MRSA in vivo. The mechanism of this beneficial drug interaction is unknown. However, Q-D-beta-lactam combinations might be useful for the treatment of complicated infections caused by multiple organisms, including MRSA.
Figures


References
-
- Amsterdam D. Susceptibility testing of antimicrobials in liquid media. In: Lorian V, editor. Antibiotics in laboratory medicine. Baltimore, Md: The Williams & Wilkins Co.; 1996. pp. 52–111.
-
- Blanc D S, Petignat C, Moreillon P, Entenza J M, Eisenring M C, Kleiber H, Wenger A, Troillet N, Blanc C H, Francioli P. Unusual spread of a penicillin-susceptible methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clone in a geographic area of low incidence. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:1512–1518. - PubMed
-
- Brumfitt W, Hamilton-Miller J M, Shah S. In-vitro activity of RP 59500, a new semisynthetic streptogramin antibiotic, against gram-positive bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992;30(Suppl. A):29–37. - PubMed
-
- Chin N X, Neu H C. Post-antibiotic effect of the new streptogramin RP 59500. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992;11:642–645. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

