Role of putative loops 2 and 3 in imipenem passage through the specific porin OprD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 10858367
- PMCID: PMC89998
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.7.1983-1985.2000
Role of putative loops 2 and 3 in imipenem passage through the specific porin OprD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
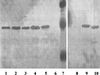
Mutant proteins with eight amino acid deletions in putative surface loops 2 and 3 of the imipenem-specific porin OprD of Pseudomonas aeruginosa failed to reconstitute imipenem susceptibility in an oprD-deficient background. The loop 3 deletion prevented the ability of imipenem to inhibit KCl conductance through the OprD channel, as previously shown for a loop 2 deletion. This suggests that both loops 2 and 3 have a role in imipenem binding to the OprD channel.
Figures


References
-
- Amsterdam D. Susceptibility testing of antimicrobials in liquid media. In: Lorian V, editor. Antibiotics in laboratory medicine. Baltimore, Md: The Williams & Wilkins Co.; 1991. pp. 72–78.
-
- Cowan S W, Schirmer T, Rummel G, Steiert M, Ghosh R, Pauptit R A, Jansonius J N, Rosenbusch J P. Crystal structures explain functional properties of two E. coli porins. Nature. 1992;358:727–733. - PubMed
-
- Cowan S W, Garavito R M, Jansonius J N, Jenkins J A, Karlsson R, König N, Pai E F, Pauptit R A, Rizkallah P J, Rosenbusch J P. The structure of OmpF porin in a tetragonal crystal form. Structure. 1995;3:1041–1050. - PubMed
-
- Huang H, Jeanteur D, Pattus F, Hancock R E W. Membrane topology and site-specific mutagenesis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa porin OprD. Mol Microbiol. 1995;16:931–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

