Mycobacterium avium grown in Acanthamoeba castellanii is protected from the effects of antimicrobials
- PMID: 10858369
- PMCID: PMC90000
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.44.7.1990-1994.2000
Mycobacterium avium grown in Acanthamoeba castellanii is protected from the effects of antimicrobials
Abstract
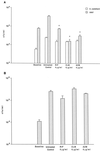
Mycobacterium avium is a common cause of systemic bacterial infection in patients with AIDS. Infection with M. avium has been linked to bacterial colonization of domestic water supplies and commonly occurs through the gastrointestinal tract. Acanthamoeba castellanii, a waterborne protozoan, may serve as an environmental host for M. avium. It has been shown that growth of M. avium in amoebae enhances invasion and intracellular replication of the bacteria in human macrophages and intestinal epithelial cell line HT-29 as well as in mice. We determined that growth of M. avium within A. castellanii influenced susceptibility to rifabutin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin. No significant activity against M. avium was seen with rifabutin, azithromycin, and clarithromycin when used to treat monolayers on both day 1 and day 4 after infection. When tested in a macrophage-like cell line (U937), all compounds showed significant anti-M. avium activity. Growth of M. avium in amoebae appears to reduce the effectiveness of the antimicrobials. These findings may have significant implications for prophylaxis of M. avium infection in AIDS.
Figures


References
-
- Bermudez L E, Inderlied C B, Kolonoski P, Wu M, Barbara-Burnham L, Young L S. Activities of Bay Y 3118, levofloxacin, and ofloxacin alone or in combination with ethambutol against Mycobacterium avium complex in vitro, in human macrophages, and in beige mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1996;40:546–551. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bermudez L E, Petrofsky M, Kolonoski P, Young L S. An animal model of Mycobacterium avium complex disseminated infection after colonization of the intestinal tract. J Infect Dis. 1992;165:75–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

