GLUT8 is a glucose transporter responsible for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in the blastocyst
- PMID: 10860996
- PMCID: PMC16542
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.13.7313
GLUT8 is a glucose transporter responsible for insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in the blastocyst
Abstract
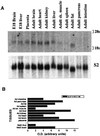
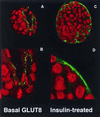
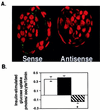
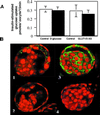
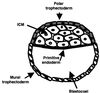
Mammalian preimplantation blastocysts exhibit insulin-stimulated glucose uptake despite the absence of the only known insulin-regulated transporter, GLUT4. We describe a previously unidentified member of the mammalian facilitative GLUT superfamily that exhibits approximately 20-25% identity with other murine facilitative GLUTs. Insulin induces a change in the intracellular localization of this protein, which translates into increased glucose uptake into the blastocyst, a process that is inhibited by antisense oligoprobes. Presence of this transporter may be necessary for successful blastocyst development, fuel metabolism, and subsequent implantation. Moreover, the existence of an alternative transporter may explain examples in other tissues of insulin-regulated glucose transport in the absence of GLUT4.
Figures

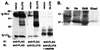
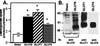
References
-
- Moley K H, Chi M M-Y, Mueckler M M. Am J Physiol. 1998;275:E38–E47. - PubMed
-
- Hogan A, Heyner S, Charron M J, Copeland N G, Gilbert D J, Jenkins M A, Thorens B, Schultz G A. Development (Cambridge, UK) 1991;113:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Aghayan M, Rao L V, Smith R M, Jarett L, Charron M J, Thorens B, Heyner S. Development (Cambridge, UK) 1992;115:305–312. - PubMed
-
- Moley K H, Chi M M-Y, Knudson C M, Korsmeyer S J, Mueckler M M. Nat Med. 1998;12:1421–1424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

