Steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) mediates the development of sex-specific brain morphology and behavior
- PMID: 10861018
- PMCID: PMC16583
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.97.13.7551
Steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1) mediates the development of sex-specific brain morphology and behavior
Abstract
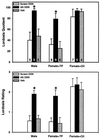
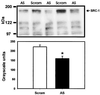
Steroid hormone action during brain development exerts profound effects on reproductive physiology and behavior that last into adulthood. A variety of in vitro studies indicate that steroid receptors require nuclear receptor coactivators for efficient transcriptional activity. To determine the functional significance of the nuclear receptor coactivator SRC-1 in developing brain, we investigated the consequence of reducing SRC-1 protein during sexual differentiation of the brain. We report that reducing SRC-1 protein interferes with the defeminizing actions of estrogen in neonatal rat brain. Our data indicate that SRC-1 protein expression is critically involved in the hormone-dependent development of normal male reproductive behavior and brain morphology.
Figures


References
-
- Tsai M J, O'Malley B W. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. - PubMed
-
- Tenbaum S, Baniahmad A. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;29:1325–1341. - PubMed
-
- Brown T R. Prostate Suppl. 1996;6:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Toppari J, Skakkebaek N E. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;12:143–156. - PubMed
-
- Hsiao P W, Lin D L, Nakao R, Chang C. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:20229–20234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

