Norwalk virus open reading frame 3 encodes a minor structural protein
- PMID: 10864672
- PMCID: PMC112168
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.14.6581-6591.2000
Norwalk virus open reading frame 3 encodes a minor structural protein
Abstract
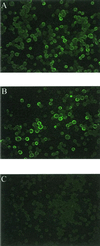
Norwalk virus (NV) is a causative agent of acute epidemic nonbacterial gastroenteritis in humans. The inability to cultivate NV has required the use of molecular techniques to examine the genome organization and functions of the viral proteins. The function of the NV protein encoded by open reading frame 3 (ORF 3) has been unknown. In this paper, we report the characterization of the NV ORF 3 protein expressed in a cell-free translation system and in insect cells and show its association with recombinant virus-like particles (VLPs) and NV virions. Expression of the ORF 3 coding region in rabbit reticulocyte lysates resulted in the production of a single protein with an apparent molecular weight of 23,000 (23K protein), which is not modified by N-linked glycosylation. The ORF 3 protein was expressed in insect cells by using two different baculovirus recombinants; one recombinant contained the entire 3' end of the genome beginning with the ORF 2 coding sequences (ORFs 2+3), and the second recombinant contained ORF 3 alone. Expression from the construct containing both ORF 2 and ORF 3 resulted in the expression of a single protein (23K protein) detected by Western blot analysis with ORF 3-specific peptide antisera. However, expression from a construct containing only the ORF 3 coding sequences resulted in the production of multiple forms of the ORF 3 protein ranging in size from 23,000 to 35,000. Indirect-immunofluorescence studies using an ORF 3 peptide antiserum showed that the ORF 3 protein is localized to the cytoplasm of infected insect cells. The 23K ORF 3 protein was consistently associated with recombinant VLPs purified from the media of insect cells infected with a baculovirus recombinant containing the entire 3' end of the NV genome. Western blot analysis of NV purified from the stools of NV-infected volunteers revealed the presence of a 35K protein as well as multiple higher-molecular-weight bands specifically recognized by an ORF 3 peptide antiserum. These results indicate that the ORF 3 protein is a minor structural protein of the virion.
Figures
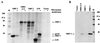
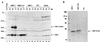





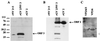
References
-
- Au K-S, Mattion N M, Estes M K. A subviral particle binding domain on the rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. Virology. 1993;194:665–673. - PubMed
-
- Ball J M, Tian P, Zeng C Q-Y, Morris A, Estes M K. Age-dependent diarrhea is induced by a viral nonstructural glycoprotein. Science. 1996;272:101–104. - PubMed
-
- Brierley I. Ribosomal frameshifting viral RNAs. J Gen Virol. 1995;76:1885–1892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

