Activation of protein kinase B by the A(1)-adenosine receptor in DDT(1)MF-2 cells
- PMID: 10864894
- PMCID: PMC1572146
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703396
Activation of protein kinase B by the A(1)-adenosine receptor in DDT(1)MF-2 cells
Abstract
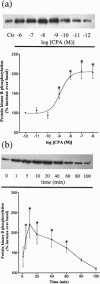
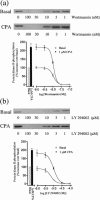
In this study the effect of insulin and A(1)-adenosine receptor stimulation on protein kinase B (PKB) activation has been investigated in the hamster vas deferens smooth muscle cell line DDT(1)MF-2. Increases in PKB phosphorylation were determined by Western blotting using an antibody that detects PKB phosphorylation at Ser(473). Insulin, a recognized activator of PKB, stimulated a concentration-dependent increase in PKB phosphorylation in DDT(1)MF-2 cells (EC(50) 5+/-1 pM). The selective A(1)-adenosine receptor agonist N(6)-cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) stimulated time and concentration-dependent increases in PKB phosphorylation in DDT(1)MF-2 cells (EC(50) 1.3+/-0.5 nM). CPA-mediated increases in PKB phosphorylation were antagonized by the A(1)-adenosine receptor selective antagonist 1,3-dipropylcyclopentylxanthine (DPCPX) yielding an apparent K(D) value of 2.3 nM. Pre-treatment of DDT(1)MF-2 cells with pertussis toxin (PTX, 100 ng ml(-1) for 16 h), to block G(i)/G(o)-dependent pathways, abolished CPA (1 microM) induced phosphorylation of PKB. In contrast, responses to insulin (100 nM) were resistant to PTX pre-treatment. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI-3K) inhibitors wortmannin (IC(50) 10.3+/-0.6 nM) and LY 294002 (IC(50) 10.3+/-1.2 microM) attenuated the phosphorylation of PKB elicited by CPA (1 microM) in a concentration-dependent manner. Wortmannin (30 nM) and LY 294002 (30 microM) also blocked responses to insulin (100 nM). Removal of extracellular Ca(2+) and chelation of intracellular Ca(2+) with BAPTA had no significant effect on CPA-induced PKB phosphorylation. Similarly, pretreatment (30 min) with inhibitors of protein kinase C (Ro 31-8220; 10 microM), tyrosine kinase (genistein; 100 microM), mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase kinase (PD 98059; 50 microM) and p38 MAPK (SB 203580; 20 microM) had no significant effect on CPA-induced PKB phosphorylation. In conclusion, these data demonstrate that A(1)-adenosine receptor stimulation in DDT(1)MF-2 cells increases PKB phosphorylation through a PTX and PI-3K-sensitive pathway.
Figures





References
-
- BERRIDGE M.J. Inositol triphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- BUTLER A.P., MARTINEZ L.A. , MONTGOMERY R.L. Involvement of a pertussis-toxin sensitive G protein in the induction of gene expression by insulin. Cell. Signal. 1996;8:475–480. - PubMed
-
- CARDONE M.H., ROY N., STENNICKE H.R., SALVESEN G.S., FRANKE T.F., STANBRIDGE E., FRISCH S. , REED J.C. Regulation of cell death protease caspase 9 by phosphorylation. Science. 1998;282:1318–1321. - PubMed
-
- CROSS D.A.E., ALESSI D.R., COHEN P., ANDJELKOVIC M. , HEMMINGS B.A. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated protein kinase B. Nature. 1995;378:785–789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

