Characterization using FLIPR of rat vanilloid receptor (rVR1) pharmacology
- PMID: 10864900
- PMCID: PMC1572142
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703390
Characterization using FLIPR of rat vanilloid receptor (rVR1) pharmacology
Abstract
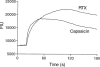
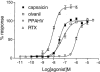
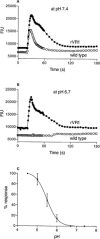
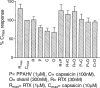
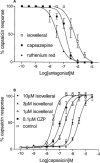
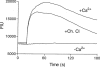
The vanilloid receptor (VR1) is a ligand-gated ion channel, which plays an important role in nociceptive processing. Therefore, a pharmacological characterization of the recently cloned rat VR1 (rVR1) was undertaken. HEK293 cells stable expressing rVR1 (rVR1-HEK293) were loaded with Fluo-3AM and then incubated at 25 degrees C for 30 min with or without various antagonists or signal transduction modifying agents. Then intracellular calcium concentrations ([Ca(2+)](i)) were monitored using FLIPR, before and after the addition of various agonists. The rank order of potency of agonists (resiniferatoxin (RTX)>capsaicin>olvanil>PPAHV) was as expected, and all were full agonists. The potencies of capsaicin and olvanil, but not RTX or PPAHV, were enhanced at pH 6.4 (pEC(50) values of 7.47+/-0.06, 7.16+/-0.06, 8.19+/-0.06 and 6.02+/-0.03 respectively at pH 7.4 vs 7.71+/-0.05, 7.58+/-0.14, 8.10+/-0.05 and 6.04+/-0.08 at pH 6.4). Capsazepine, isovelleral and ruthenium red all inhibited the capsaicin (100 nM)-induced Ca(2+) response in rVR1-HEK293 cells, with pK(B) values of 7.52+/-0.08, 6.92+/-0.11 and 8.09+/-0.12 respectively (n=6 each). The response to RTX and olvanil were also inhibited by these compounds. None displayed any agonist-like activity. The removal of extracellular Ca(2+) abolished, whilst inhibition of protein kinase C with chelerythrine chloride (10 microM) partially (approximately 20%) inhibited, the capsaicin (10 microM)-induced Ca(2+) response. However, tetrodotoxin (3 microM), nimodipine (10 microM), omega-GVIA conotoxin (1 microM), thapsigargin (1 microM), U73122 (3 microM) or H-89 (3 microM) had no effect on the capsaicin (100 nM)-induced response. In conclusion, the recombinant rVR1 stably expressed in HEK293 cells acts as a ligand-gated Ca(2+) channel with the appropriate agonist and antagonist pharmacology, and therefore is a suitable model for studying the effects of drugs at this receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterisation using FLIPR of human vanilloid VR1 receptor pharmacology.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Apr 6;417(1-2):51-8. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)00901-3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11301059
-
Pharmacology of vanilloids at recombinant and endogenous rat vanilloid receptors.Biochem Pharmacol. 2003 Jan 1;65(1):143-51. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(02)01451-x. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12473388
-
Use of a fluorescent imaging plate reader--based calcium assay to assess pharmacological differences between the human and rat vanilloid receptor.J Biomol Screen. 2002 Oct;7(5):466-75. doi: 10.1177/108705702237679. J Biomol Screen. 2002. PMID: 14599363
-
Cloning and pharmacological characterization of mouse TRPV1.Neurosci Lett. 2004 Nov 3;370(1):55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2004.07.058. Neurosci Lett. 2004. PMID: 15489017
-
Identification of species-specific determinants of the action of the antagonist capsazepine and the agonist PPAHV on TRPV1.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 23;279(17):17165-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313328200. Epub 2004 Feb 11. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14960593
Cited by
-
Anandamide is a partial agonist at native vanilloid receptors in acutely isolated mouse trigeminal sensory neurons.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Oct;137(4):421-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704904. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 12359623 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of piperine, the pungent component of black pepper, at the human vanilloid receptor (TRPV1).Br J Pharmacol. 2005 Mar;144(6):781-90. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706040. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15685214 Free PMC article.
-
Increased function of the TRPV1 channel in small sensory neurons after local inflammation or in vitro exposure to the pro-inflammatory cytokine GRO/KC.Neurosci Bull. 2012 Apr;28(2):155-64. doi: 10.1007/s12264-012-1208-8. Neurosci Bull. 2012. PMID: 22466126 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological differences between the human and rat vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1).Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;132(5):1084-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703918. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11226139 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of acid-induced activation of airway afferent nerve fibres in guinea-pig.J Physiol. 2002 Sep 1;543(Pt 2):591-600. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.022848. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12205192 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACS G., LEE J., MARQUEZ V. , BLUMBERG P.M. Distinctstructure-activity relations for stimulation of 45Ca uptake and high affinity binding in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurons and dorsal root ganglion membranes. Mol. Brain Res. 1996;35:173–182. - PubMed
-
- APPENDINO G., CRAVOTTO G., PALMISANO G., ANNUNZIATA R. , SZALLASI A. Synthesis and evaluation of phoboid-20-homovanillates. Discovery of a class of ligand binding to the vanilloid receptor with different degrees of cooperativity. J. Med. Chem. 1996;39:3123–3131. - PubMed
-
- BAUMANN T.K., BURCHIEL K.J., INGRAM S.L. , MARTENSON M.E. Responses of adult human dorsal root ganglion neurons in culture to capsaicin and low pH. Pain. 1996;65:31–38. - PubMed
-
- BELTRAMO M. , PIOMELLI D. Anandamide transport inhibition by the vanilloid agonist olvanil. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999;364:75–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

