SNPing away at complex diseases: analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphisms around APOE in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 10869235
- PMCID: PMC1287185
- DOI: 10.1086/303003
SNPing away at complex diseases: analysis of single-nucleotide polymorphisms around APOE in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
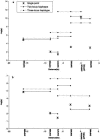
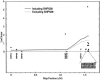
There has been great interest in the prospects of using single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the search for complex disease genes, and several initiatives devoted to the identification and mapping of SNPs throughout the human genome are currently underway. However, actual data investigating the use of SNPs for identification of complex disease genes are scarce. To begin to look at issues surrounding the use of SNPs in complex disease studies, we have initiated a collaborative SNP mapping study around APOE, the well-established susceptibility gene for late-onset Alzheimer disease (AD). Sixty SNPs in a 1.5-Mb region surrounding APOE were genotyped in samples of unrelated cases of AD, in controls, and in families with AD. Standard tests were conducted to look for association of SNP alleles with AD, in cases and controls. We also used family-based association analyses, including recently developed methods to look for haplotype association. Evidence of association (P</=.05) was identified for 7 of 13 SNPs, including the APOE-4 polymorphism, spanning 40 kb on either side of APOE. As expected, very strong evidence for association with AD was seen for the APOE-4 polymorphism, as well as for two other SNPs that lie <16 kb from APOE. Haplotype analysis using family data increased significance over that seen in single-locus tests for some of the markers, and, for these data, improved localization of the gene. Our results demonstrate that associations can be detected at SNPs near a complex disease gene. We found that a high density of markers will be necessary in order to have a good chance of including SNPs with detectable levels of allelic association with the disease mutation, and statistical analysis based on haplotypes can provide additional information with respect to tests of significance and fine localization of complex disease genes.
Figures
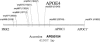


References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/GenbankOverview.html (for cosmid sequences)
-
- GDA: Software for the Analysis of Discrete Genetic Data, http://alleyn.eeb.uconn.edu/gda
-
- LocusLink, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/LocusLink (for TOM40 [accession number 10452])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim (for AD [MIM 104300] and APOE [MIM 107741])
References
-
- Ashworth LK, Batzer MA, Brandriff B, Branscomb E, De Jong P, Garcia E, Garnes JA, et al (1995) An integrated metric physical map of human chromosome 19. Nat Genet 11:422–427 - PubMed
-
- Blacker D, Haines JL, Rodes L, Terwedow H, Go RCP, Harrell LE, Perry RT, et al (1997) ApoE-4 and age at onset of Alzheimer's disease: the NIMH genetics initiative. Neurology 48:139–147 - PubMed
-
- Collins FS, Brooks LD, Chakravarti A (1998) A DNA polymorphism discovery resource for research on human genetic variation. Genome Res 8:1229–1231 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

