Role of EGR1 in hippocampal synaptic enhancement induced by tetanic stimulation and amputation
- PMID: 10871275
- PMCID: PMC2175137
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.7.1325
Role of EGR1 in hippocampal synaptic enhancement induced by tetanic stimulation and amputation
Abstract
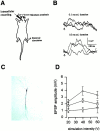
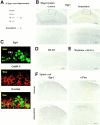
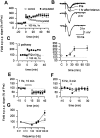
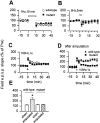
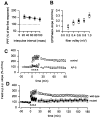
Hippocampal neurons fire spikes when an animal is at a particular location or performs certain behaviors in a particular place, providing a cellular basis for hippocampal involvement in spatial learning and memory. In a natural environment, spatial memory is often associated with potentially dangerous sensory experiences such as noxious or painful stimuli. The central sites for such pain-associated memory or plasticity have not been identified. Here we present evidence that excitatory glutamatergic synapses within the CA1 region of the hippocampus may play a role in storing pain-related information. Peripheral noxious stimulation induced excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) in CA1 pyramidal cells in anesthetized animals. Tissue/nerve injury caused a rapid increase in the level of the immediate-early gene product Egr1 (also called NGFI-A, Krox24, or zif/268) in hippocampal CA1 neurons. In parallel, synaptic potentiation induced by a single tetanic stimulation (100 Hz for 1 s) was enhanced after the injury. This enhancement of synaptic potentiation was absent in mice lacking Egr1. Our data suggest that Egr1 may act as an important regulator of pain-related synaptic plasticity within the hippocampus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Subfield-specific immediate early gene expression associated with hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo.Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Mar;13(5):968-76. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01467.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11264669
-
Prenatal administration of morphine decreases CREBSerine-133 phosphorylation and synaptic plasticity range mediated by glutamatergic transmission in the hippocampal CA1 area of cognitive-deficient rat offspring.Hippocampus. 2003;13(8):915-21. doi: 10.1002/hipo.10137. Hippocampus. 2003. PMID: 14750654
-
Long-term potentiation and long-term depression in hippocampal CA1 neurons of mice lacking the IP(3) type 1 receptor.Neuroscience. 2003;117(4):821-30. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00803-5. Neuroscience. 2003. PMID: 12654335
-
Muscarinic Receptors, from Synaptic Plasticity to its Role in Network Activity.Neuroscience. 2021 Feb 21;456:60-70. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.04.005. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Neuroscience. 2021. PMID: 32278062 Review.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of protein kinase ζ in the maintenance of hippocampal long-term potentiation in rats with chronic visceral hypersensitivity.J Neurophysiol. 2015 May 1;113(9):3047-55. doi: 10.1152/jn.00929.2014. Epub 2015 Mar 11. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25761958 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical depression and potentiation: basic mechanisms for phantom pain.Exp Neurobiol. 2012 Dec;21(4):129-35. doi: 10.5607/en.2012.21.4.129. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Exp Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 23319872 Free PMC article.
-
Formalin pain increases the concentration of serotonin and its 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid metabolite in the CA1 region of hippocampus.Daru. 2010;18(1):29-34. Daru. 2010. PMID: 22615590 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of T-type calcium channel CaV3.2: bi-directionality by early growth response 1 (Egr1) and repressor element 1 (RE-1) protein-silencing transcription factor (REST).J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15489-501. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.310763. Epub 2012 Mar 19. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22431737 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of synaptic synchrony on the neuronal input-output relationship.Neural Comput. 2008 Jul;20(7):1717-31. doi: 10.1162/neco.2008.10-06-385. Neural Comput. 2008. PMID: 18254692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aloisi A.M., Zimmermann M., Herdegen T. Sex-dependent effects of formalin and restraint on c-Fos expression in the septum and hippocampus of the rat. Neuroscience. 1997;81:951–958. - PubMed
-
- Bear M.F., Malenka R.C. Synaptic plasticityLTP and LTD. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1994;4:389–399. - PubMed
-
- Berger T.W., Alger B., Thompson R.F. Neuronal substrate of classical conditioning in the hippocampus. Science. 1976;192:483–485. - PubMed
-
- Berger T.W., Laham R.I., Thompson R.F. Hippocampal unit-behavior correlations during classical conditioning. Brain Res. 1980;193:229–248. - PubMed
-
- Berger T.W., Rinaldi P.C., Weisz D.J., Thompson R.F. Single-unit analysis of different hippocampal cell types during classical conditioning of rabbit nictitating membrane response. J. Neurophysiol. 1983;50:1197–1219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

