Cdc28 activates exit from mitosis in budding yeast
- PMID: 10871278
- PMCID: PMC2175138
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.7.1361
Cdc28 activates exit from mitosis in budding yeast
Abstract
The activity of the cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1), Cdc28, inhibits the transition from anaphase to G1 in budding yeast. CDC28-T18V, Y19F (CDC28-VF), a mutant that lacks inhibitory phosphorylation sites, delays the exit from mitosis and is hypersensitive to perturbations that arrest cells in mitosis. Surprisingly, this behavior is not due to a lack of inhibitory phosphorylation or increased kinase activity, but reflects reduced activity of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC), a defect shared with other mutants that lower Cdc28/Clb activity in mitosis. CDC28-VF has reduced Cdc20- dependent APC activity in mitosis, but normal Hct1- dependent APC activity in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. The defect in Cdc20-dependent APC activity in CDC28-VF correlates with reduced association of Cdc20 with the APC. The defects of CDC28-VF suggest that Cdc28 activity is required to induce the metaphase to anaphase transition and initiate the transition from anaphase to G1 in budding yeast.
Figures

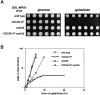
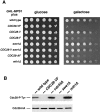

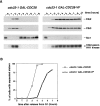



References
-
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae . Nature. 1992;355:368–371. - PubMed
-
- Bishop A.C., Ubersax J.A., Petsch D.T., Matheos D.P., Gray N.S., Blethrow J., Shimizu E., Tsien J.Z., Schultz P.G., Rose M.D. A chemical switch for inhibitor-sensitive alleles of any protein kinase. Nature. 2000;In press - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

