GAP43, MARCKS, and CAP23 modulate PI(4,5)P(2) at plasmalemmal rafts, and regulate cell cortex actin dynamics through a common mechanism
- PMID: 10871285
- PMCID: PMC2175130
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.7.1455
GAP43, MARCKS, and CAP23 modulate PI(4,5)P(2) at plasmalemmal rafts, and regulate cell cortex actin dynamics through a common mechanism
Abstract
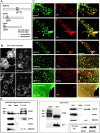
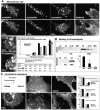
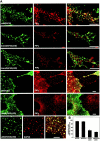
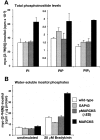
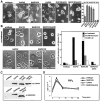
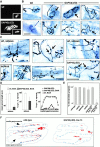
The dynamic properties of the cell cortex and its actin cytoskeleton determine important aspects of cell behavior and are a major target of cell regulation. GAP43, myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS), and CAP23 (GMC) are locally abundant, plasmalemma-associated PKC substrates that affect actin cytoskeleton. Their expression correlates with morphogenic processes and cell motility, but their role in cortex regulation has been difficult to define mechanistically. We now show that the three proteins accumulate at rafts, where they codistribute with PI(4,5)P(2), and promote its retention and clustering. Binding and modulation of PI(4, 5)P(2) depended on the basic effector domain (ED) of these proteins, and constructs lacking the ED functioned as dominant inhibitors of plasmalemmal PI(4,5)P(2) modulation. In the neuron-like cell line, PC12, NGF- and substrate-induced peripheral actin structures, and neurite outgrowth were greatly augmented by any of the three proteins, and suppressed by DeltaED mutants. Agents that globally mask PI(4,5)P(2) mimicked the effects of GMC on peripheral actin recruitment and cell spreading, but interfered with polarization and process formation. Dominant negative GAP43(DeltaED) also interfered with peripheral nerve regeneration, stimulus-induced nerve sprouting and control of anatomical plasticity at the neuromuscular junction of transgenic mice. These results suggest that GMC are functionally and mechanistically related PI(4,5)P(2) modulating proteins, upstream of actin and cell cortex dynamics regulation.
Figures



References
-
- Aderem A. The MARCKS family of protein kinase-C substrates. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1995;23:587–591. - PubMed
-
- Aigner L., Arber S., Kapfhammer J.P., Laux T., Schneider C., Botteri F., Brenner H.-R., Caroni P. Overexpression of the neural growth-associated protein GAP-43 induces nerve sprouting in the adult nervous system of transgenic mice. Cell. 1995;83:269–278. - PubMed
-
- Arber S., Barbayannis T.A., Hanser H, Schneider C., Stanyon C.A., Bernard O., Caroni P. Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature. 1998;393:805–809. - PubMed
-
- Baetge E.E., Hammang J.P. Neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells deficient in GAP-43. Neuron. 1991;6:21–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

