Activity-dependent neuronal control of gap-junctional communication in astrocytes
- PMID: 10871289
- PMCID: PMC2175141
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.149.7.1513
Activity-dependent neuronal control of gap-junctional communication in astrocytes
Abstract
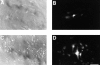
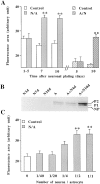
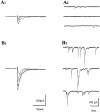
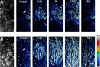
A typical feature of astrocytes is their high degree of intercellular communication through gap junction channels. Using different models of astrocyte cultures and astrocyte/neuron cocultures, we have demonstrated that neurons upregulate gap-junctional communication and the expression of connexin 43 (Cx43) in astrocytes. The propagation of intercellular calcium waves triggered in astrocytes by mechanical stimulation was also increased in cocultures. This facilitation depends on the age and number of neurons, indicating that the state of neuronal differentiation and neuron density constitute two crucial factors of this interaction. The effects of neurons on astrocytic communication and Cx43 expression were reversed completely after neurotoxic treatments. Moreover, the neuronal facilitation of glial coupling was suppressed, without change in Cx43 expression, after prolonged pharmacological treatments that prevented spontaneous synaptic activity. Altogether, these results demonstrate that neurons exert multiple and differential controls on astrocytic gap-junctional communication. Since astrocytes have been shown to facilitate synaptic efficacy, our findings suggest that neuronal and astrocytic networks interact actively through mutual setting of their respective modes of communication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Astrocytes in 17beta-estradiol treated mixed hippocampal cultures show attenuated calcium response to neuronal activity.Glia. 2006 Jun;53(8):817-26. doi: 10.1002/glia.20341. Glia. 2006. PMID: 16565986
-
Brain macrophages inhibit gap junctional communication and downregulate connexin 43 expression in cultured astrocytes.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Jan;15(2):403-7. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01868.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11849308
-
Neurons set the tone of gap junctional communication in astrocytic networks.Neurochem Int. 2004 Jul-Aug;45(2-3):265-72. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2003.07.004. Neurochem Int. 2004. PMID: 15145542 Review.
-
Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide enhances ATP/gap junction-mediated calcium-wave propagation in astrocytes.Neuromolecular Med. 2003;3(3):173-80. doi: 10.1385/NMM:3:3:173. Neuromolecular Med. 2003. PMID: 12835512
-
Astrocyte responses to neuronal activity.Glia. 2004 Aug 15;47(3):226-232. doi: 10.1002/glia.20029. Glia. 2004. PMID: 15252811 Review.
Cited by
-
Astroglial Cx30 sustains neuronal population bursts independently of gap-junction mediated biochemical coupling.Glia. 2019 Jun;67(6):1104-1112. doi: 10.1002/glia.23591. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Glia. 2019. PMID: 30794327 Free PMC article.
-
The role of astrocytes in mediating exogenous cell-based restorative therapy for stroke.Glia. 2014 Jan;62(1):1-16. doi: 10.1002/glia.22585. Epub 2013 Nov 4. Glia. 2014. PMID: 24272702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational models of neuron-astrocyte interaction in epilepsy.Front Comput Neurosci. 2012 Aug 13;6:58. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2012.00058. eCollection 2012. Front Comput Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23060780 Free PMC article.
-
The Gliocentric Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 5;19(10):3033. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103033. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30301132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fast and reversible stimulation of astrocytic glycolysis by K+ and a delayed and persistent effect of glutamate.J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 23;31(12):4709-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5311-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21430169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araque A., Parpura V., Sanzgiri R.P., Haydon P.G. Glutamate-dependent astrocyte modulation of synaptic transmission between cultured hippocampal neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998;10:2129–2142. - PubMed
-
- Araque A., Parpura V., Sanzgiri R.P., Haydon P.G. Tripartite synapsesglia, the unacknowledged partner. TINS. 1999;22:208–215. - PubMed
-
- Bacci A., Verderio C., Pravettoni E., Matteoli M. Synaptic and intrinsic mechanisms shape synchronous oscillations in hippocampal neurons in culture. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999;11:389–397. - PubMed
-
- Bezzi P., Carmignoto G., Pasti L., Vesce S., Rossi D., Lodi Rizzini B., Pozzan T., Volterra A. Prostaglandins stimulate calcium-dependent glutamate release in astrocytes. Nature. 1998;391:281–285. - PubMed
-
- Bruzzone R., Giaume C. Connexins and information transfer through glia. In: Matsas R., Tsacoupoulos M., editors. The Functional Roles of Glial Cells in Health and Disease. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; New York: 1999. pp. 321–337. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

