T cell-mediated Fas-induced keratinocyte apoptosis plays a key pathogenetic role in eczematous dermatitis
- PMID: 10880045
- PMCID: PMC517909
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI9199
T cell-mediated Fas-induced keratinocyte apoptosis plays a key pathogenetic role in eczematous dermatitis
Abstract
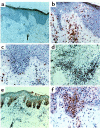
Clinical and histologic similarities between various eczematous disorders point to a common efferent pathway. We demonstrate here that activated T cells infiltrating the skin in atopic dermatitis (AD) and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) induce keratinocyte (KC) apoptosis. KCs normally express low levels of Fas receptor (FasR) that can be substantially enhanced by the presence of IFN-gamma. KCs are rendered susceptible to apoptosis by IFN-gamma when FasR numbers reach a threshold of approximately 40,000 per KC. Subsequently, KCs undergo apoptosis induced by anti-FasR mAb's, soluble Fas ligand, supernatants from activated T cells, or direct contact between T cells and KCs. Apoptotic KCs show typical DNA fragmentation and membrane phosphatidylserine expression. KC apoptosis was demonstrated in situ in lesional skin affected by AD, ACD, and patch tests. Using numerous cytokines and anti-cytokine neutralizing mAb's, we found no evidence that cytokines other than IFN-gamma participate in this process. In addition, apoptosis-inducing pathways other than FasR triggering were ruled out by blocking T cell-induced KC apoptosis by caspase inhibitors and soluble Fas-Fc protein. Responses of normal human skin and cultured skin equivalents to activated T cells demonstrated that KC apoptosis caused by skin-infiltrating T cells is a key event in the pathogenesis of eczematous dermatitis.
Figures





Comment in
-
No eczema without keratinocyte death.J Clin Invest. 2000 Jul;106(1):9-10. doi: 10.1172/JCI10438. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10880042 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Singer KH, Tuck DT, Sampson HA, Hall RP. Epidermal keratinocytes express the adhesion molecule intracellular adhesion molecule-1 in inflammatory dermatoses. J Invest Dermatol. 1989;92:746–750. - PubMed
-
- Bieber T, Dannenberg B, Ring J, Braun-Falco O. Keratinocytes in lesional skin of atopic eczema bear HLA-DR, CD1a and IgE molecules. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1989;14:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Leung DY. Pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;104(Suppl.):S99–S108. - PubMed
-
- Rudikoff D, Lebwohl M. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet. 1998;351:1715–1721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

