Targeted deletion of matrix metalloproteinase-9 attenuates left ventricular enlargement and collagen accumulation after experimental myocardial infarction
- PMID: 10880048
- PMCID: PMC517910
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8768
Targeted deletion of matrix metalloproteinase-9 attenuates left ventricular enlargement and collagen accumulation after experimental myocardial infarction
Abstract
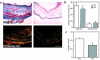
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) is prominently overexpressed after myocardial infarction (MI). We tested the hypothesis that mice with targeted deletion of MMP9 have less left ventricular (LV) dilation after experimental MI than do sibling wild-type (WT) mice. Animals that survived ligation of the left coronary artery underwent echocardiographic studies after MI; all analyses were performed without knowledge of mouse genotype. By day 8, MMP9 knockout (KO) mice had significantly smaller increases in end-diastolic and end-systolic ventricular dimensions at both midpapillary and apical levels, compared with infarcted WT mice; these differences persisted at 15 days after MI. MMP-9 KO mice had less collagen accumulation in the infarcted area than did WT mice, and they showed enhanced expression of MMP-2, MMP-13, and TIMP-1 and a reduced number of macrophages. We conclude that targeted deletion of the MMP9 gene attenuates LV dilation after experimental MI in mice. The decrease in collagen accumulation and the enhanced expression of other MMPs suggest that MMP-9 plays a prominent role in extracellular matrix remodeling after MI.
Figures



References
-
- Pfeffer JM, Pfeffer MA, Fletcher PJ, Braunwald E. Progressive ventricular remodeling in rat with myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol. 1991;260:H1406–H1414. - PubMed
-
- Rumberger JA. Ventricular dilatation and remodeling after myocardial infarction. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994;69:664–674. - PubMed
-
- Tyagi SC, Ratajska A, Weber KT. Myocardial matrix metalloproteinase(s): localization and activation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1993;126:49–59. - PubMed
-
- Cleutjens JP, Kandala JC, Guarda E, Guntaka RV, Weber KT. Regulation of collagen degradation in the rat myocardium after infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1995;27:1281–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

