Human allograft acceptance is associated with immune regulation
- PMID: 10880058
- PMCID: PMC314359
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI9171
Human allograft acceptance is associated with immune regulation
Abstract
The ultimate goal of transplantation is drug-free allograft acceptance, which is rarely encountered in transplant recipients. Using a novel human-to-mouse "trans vivo" delayed-type hypersensitivity assay, we assessed donor-reactive cell-mediated immune responses in kidney and liver transplant patients, four of whom discontinued all immunosuppression. One of these subjects (J.B.) rejected his graft after 7 years of stable function, while the others (D.S., R.D., M.L.) continue to have excellent graft function 5, 28, and 4 years after the cessation of immunosuppression. PBMCs from J.B. exhibited strong responses to both donor and recall antigens whereas PBMCs from patients D.S., R.D., and M.L. responded strongly to recall, but not donor, antigens. Furthermore, when donor and recall antigens were colocalized, the recall response in these three patients was inhibited. This donor antigen-linked nonresponsiveness was observed in four other patients who are still maintained on immunosuppression. The weakness of donor-reactive DTH responses in these patients is due to donor alloantigen-triggered regulation that relies on either TGF-beta or IL-10. In D.S., regulation is triggered by a single donor HLA Class I antigen, either in membrane-bound or soluble form. This demonstrates that allograft acceptance in humans is associated with an immune regulation pattern, which may be useful in the diagnosis and/or monitoring of transplant patients for allograft acceptance.
Figures
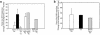
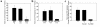
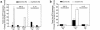
References
-
- Burlingham WJ, et al. Microchimerism linked to cytotoxic T lymphocyte functional unresponsiveness (clonal anergy) in a tolerant renal transplant recipient. Transplantation. 1995;59:1147–1155. - PubMed
-
- Zoller KM, Cho SI, Cohen JJ, Harrington JT. Cessation of immunosuppressive therapy after successful transplantation: a national survey. Kidney Int. 1980;18:110–114. - PubMed
-
- Uehling DT, Hussey JL, Weinstein AB, Wank R, Bach FH. Cessation of immunosuppression after renal transplantation. Surgery. 1976;79:278–282. - PubMed
-
- VanBuskirk AM, Wakely ME, Sirak JH, Orosz CG. Patterns of allosensitization in allograft recipients: long-term cardiac allograft acceptance is associated with active alloantibody production in conjunction with active inhibition of alloreactive delayed-type hypersensitivity. Transplantation. 1998;65:1115–1123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

