Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitor genes in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in mice
- PMID: 10880390
- PMCID: PMC1850205
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64531-2
Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitor genes in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxemia in mice
Abstract
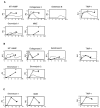
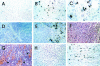
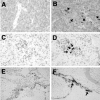
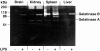
An imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and inhibitors of MMPs (TIMPs) may contribute to tissue destruction that is found in various inflammatory disorders. To determine in an in vivo experimental setting whether the inflammatory reaction in the course of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxemia causes an altered balance in the MMP/TIMP system, we analyzed the expression of a number of MMP and TIMP genes as well as MMP enzymatic activity in the liver, kidney, spleen, and brain at various time points after systemic injection of different doses of LPS in mice. Injection of sublethal doses of LPS led to an organ- and time-specific pattern of up-regulation of several MMP genes and the TIMP-1 gene in the liver, spleen, and kidney, whereas in the brain only TIMP-1 was induced. Injection of a lethal dose of LPS caused similar but more prolonged expression of these MMP genes as well as the induction of additional MMP genes in all organs. In LPS-treated mice in situ hybridization revealed collagenase 3 gene induction in cells resembling macrophages whereas TIMP-1 RNA was detected predominantly in parenchymal cells. Finally, gelatin zymography revealed increased gelatinolytic activity in all organs after LPS treatment. These observations highlight a dramatic shift in favor of increased expression of the MMP genes over the TIMP genes during LPS-induced endotoxemia, and suggest that MMPs may contribute to the development of organ damage in endotoxemia.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cell and agonist-specific regulation of genes for matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors by primary glial cells.J Neurochem. 2006 Aug;98(3):812-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03927.x. J Neurochem. 2006. PMID: 16893421
-
Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the developing neonatal mouse uterus.Biol Reprod. 2004 Nov;71(5):1598-604. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.031559. Epub 2004 Jul 7. Biol Reprod. 2004. PMID: 15240428
-
Regulation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPS) and their inhibitors (TIMPS) during mouse peri-implantation: role of nitric oxide.Placenta. 2004 Apr;25(4):243-52. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2003.08.014. Placenta. 2004. PMID: 15028415
-
The regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008;40(6-7):1362-78. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2007.12.006. Epub 2007 Dec 24. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18258475 Review.
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-4. The road less traveled.Mol Cancer. 2008 Nov 21;7:85. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-7-85. Mol Cancer. 2008. PMID: 19025595 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptors 4 induces expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human aortic smooth muscle cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Feb;38(2):1419-23. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0246-4. Epub 2010 Aug 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 20725790
-
Endotoxemia shifts neutrophils with TIMP-free gelatinase B/MMP-9 from bone marrow to the periphery and induces systematic upregulation of TIMP-1.Haematologica. 2017 Oct;102(10):1671-1682. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.168799. Epub 2017 Aug 3. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 28775117 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterial lipomannan induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in human macrophagic cells through a Toll-like receptor 1 (TLR1)/TLR2- and CD14-dependent mechanism.Infect Immun. 2005 Oct;73(10):7064-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.7064-7068.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16177394 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Epigenetic Mechanisms in the Causation of Aberrant MMP Activity during Human Pathologies and the Use of Medicinal Drugs.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 15;11(4):578. doi: 10.3390/biom11040578. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33920915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain Barrier Breakdown as a Cause and Consequence of Neuroinflammation in Sepsis.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Feb;55(2):1045-1053. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0356-7. Epub 2017 Jan 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28092082 Review.
References
-
- Lynn WA, Cohen J: Adjunctive therapy for septic shock: a review of experimental approaches. Clin Infect Dis 1995, 20:143-158 - PubMed
-
- Vogel SN, Hogan MM: Immunophysiology: The Role of Cells and Cytokines in Immunity and Inflammation. Edited by JJ Oppenheim, EM Shevach. New York, Oxford University Press, 1990, pp 238–258
-
- Hailman E, Vasselon T, Kelley M, Busse LA, Hu MC, Lichenstein HS, Detmers PA, Wright SD: Stimulation of macrophages and neutrophils by complexes of lipopolysaccharide and soluble CD14. J Immunol 1996, 156:4384-4390 - PubMed
-
- Raetz CRH, Ulevitch RJ, Wright SD, Sibley CH, Ding A, Nathan CF: Gram-negative endotoxin: an extraordinary lipid with profound effects on eukaryotic signal transduction. FASEB J 1991, 5:2652-2660 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

