Destabilization of nucleosomes by an unusual DNA conformation adopted by poly(dA) small middle dotpoly(dT) tracts in vivo
- PMID: 10880448
- PMCID: PMC313933
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.13.3358
Destabilization of nucleosomes by an unusual DNA conformation adopted by poly(dA) small middle dotpoly(dT) tracts in vivo
Abstract
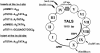
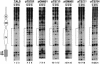
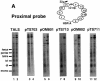
Poly(dA) small middle dotpoly(dT) tracts are common and often found upstream of genes in eukaryotes. It has been suggested that poly(dA) small middle dotpoly(dT) promotes transcription in vivo by affecting nucleosome formation. On the other hand, in vitro studies show that poly(dA) small middle dotpoly(dT) can be easily incorporated into nucleosomes. Therefore, the roles of these tracts in nucleosome organization in vivo remain to be established. We have developed an assay system that can evaluate nucleosome formation in yeast cells, and demonstrated that relatively longer tracts such as A(15)TATA(16) and A(34) disrupt an array of positioned nucleosomes, whereas a shorter A(5)TATA(4) tract is incorporated in positioned nucleosomes of yeast minichromosomes. Thus, nucleosomes are destabilized by poly(dA) small middle dotpoly(dT) in vivo in a length-dependent manner. Furthermore, in vivo UV footprinting revealed that the longer tracts adopt an unusual DNA structure in yeast cells that corresponds to the B' conformation described in vitro. Our results support a mechanism in which a unique poly(dA) small middle dot poly(dT) conformation presets chromatin structure to which transcription factors are accessible.
Figures

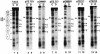

Similar articles
-
Modulation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer formation in a positioned nucleosome containing poly(dA.dT) tracts.Biochemistry. 1996 Jun 18;35(24):7705-14. doi: 10.1021/bi953011r. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8672471
-
Structure of the hydration shells of oligo(dA-dT).oligo(dA-dT) and oligo(dA).oligo(dT) tracts in B-type conformation on the basis of Monte Carlo calculations.Biopolymers. 1990;30(5-6):563-81. doi: 10.1002/bip.360300509. Biopolymers. 1990. PMID: 2265229
-
Positioned and G/C-capped poly(dA:dT) tracts associate with the centers of nucleosome-free regions in yeast promoters.Genome Res. 2010 Apr;20(4):473-84. doi: 10.1101/gr.103226.109. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Genome Res. 2010. PMID: 20133331 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(dA:dT) tracts: major determinants of nucleosome organization.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009 Feb;19(1):65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.01.004. Epub 2009 Feb 7. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19208466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Active Mechanism of Nucleosome Depletion by Poly(dA:dT) Tracts In Vivo.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 30;22(15):8233. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158233. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exposing the core promoter is sufficient to activate transcription and alter coactivator requirement at RNR3.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 May 22;104(21):8833-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0701666104. Epub 2007 May 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17502614 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of sequence-directed nucleosome disruption on cell-type-specific repression by alpha2/Mcm1 in the yeast genome.Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Nov;5(11):1925-33. doi: 10.1128/EC.00105-06. Epub 2006 Sep 15. Eukaryot Cell. 2006. PMID: 16980406 Free PMC article.
-
Telomeric repeats act as nucleosome-disfavouring sequences in vivo.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Feb;42(3):1541-52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1006. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24174540 Free PMC article.
-
Non-LTR retrotransposons and microsatellites: Partners in genomic variation.Mob Genet Elements. 2013 Jul 1;3(4):e25674. doi: 10.4161/mge.25674. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Mob Genet Elements. 2013. PMID: 24195012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A nucleosome positioned by alpha2/Mcm1 prevents Hap1 activator binding in vivo.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Dec 21;364(3):583-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.10.037. Epub 2007 Oct 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17959145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexeev D.G., Lipanov,A.A. and Skuratovskii,I.Ya. (1987) Poly(dA)⋅ poly(dT) is a B-type double helix with a distinctively narrow minor groove. Nature, 325, 821–823. - PubMed
-
- Becker P.B., Tsukiyama,T. and Wu,C. (1994) Chromatin assembly extracts from Drosophila embryos. Methods Cell Biol., 44, 207–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

