Adenovirus-specific translation by displacement of kinase Mnk1 from cap-initiation complex eIF4F
- PMID: 10880459
- PMCID: PMC313943
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.13.3465
Adenovirus-specific translation by displacement of kinase Mnk1 from cap-initiation complex eIF4F
Abstract
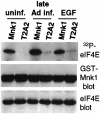
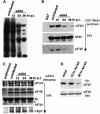
Translation of cellular mRNAs involves formation of a cap-binding translation initiation complex known as eIF4F, containing phosphorylated cap-binding protein eIF4E, eIF4E kinase Mnk1, eIF4A, poly(A)-binding protein and eIF4G. Adenovirus is shown to prevent cellular translation by displacing Mnk1 from eIF4F, thereby blocking phosphorylation of eIF4E. Over expression of an eIF4E mutant that cannot be phosphorylated by Mnk1 impairs translation of cellular but not viral late mRNAs. Adenovirus 100k protein is shown to bind the C-terminus of eIF4G in vivo and in vitro, the same region bound by Mnk1. In vivo, 100k protein displaces Mnk1 from eIF4G during adenovirus infection, or in transfected cells. Purified 100k protein also evicts Mnk1 from isolated eIF4F complexes in vitro. A mutant adenovirus with a temperature-sensitive 100k protein that cannot inhibit cellular protein synthesis at restrictive temperature no longer blocks Mnk1 binding to eIF4G, or phosphorylation of eIF4E. We describe a mechanism whereby adenovirus selectively inhibits the translation of cellular but not viral mRNAs by displacement of Mnk1 from eIF4G and inhibition of eIF4E phosphorylation.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Structural basis for competitive inhibition of eIF4G-Mnk1 interaction by the adenovirus 100-kilodalton protein.J Virol. 2004 Jul;78(14):7707-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.14.7707-7716.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15220445 Free PMC article.
-
Chaperone hsp27 inhibits translation during heat shock by binding eIF4G and facilitating dissociation of cap-initiation complexes.Genes Dev. 2000 Jun 15;14(12):1460-70. Genes Dev. 2000. PMID: 10859165 Free PMC article.
-
Human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) recruits mnk1 to phosphorylate eIF4E.EMBO J. 1999 Jan 4;18(1):270-9. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.1.270. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 9878069 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the cap-binding protein eIF4E by the MAPK-activated protein kinase Mnk1.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Oct 15;60(8):1237-43. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00429-9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11007962 Review.
-
eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation.Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:913-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.913. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10872469 Review.
Cited by
-
Viral strategies of translation initiation: ribosomal shunt and reinitiation.Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2002;72:1-39. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(02)72066-7. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12206450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influenza virus mRNA translation revisited: is the eIF4E cap-binding factor required for viral mRNA translation?J Virol. 2007 Nov;81(22):12427-38. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01105-07. Epub 2007 Sep 12. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17855553 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a cis-acting element required for shunt-mediated translational initiation of the Sendai virus Y proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Jan 15;31(2):608-18. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg143. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 12527769 Free PMC article.
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F architectural alterations accompany translation initiation factor redistribution in poxvirus-infected cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Apr;28(8):2648-58. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01631-07. Epub 2008 Feb 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18250159 Free PMC article.
-
The adenovirus E1B 55-kilodalton and E4 open reading frame 6 proteins limit phosphorylation of eIF2alpha during the late phase of infection.J Virol. 2009 Oct;83(19):9970-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01113-09. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19605483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonneau A.M. and Sonenberg,N. (1987) Involvement of the 24kd cap-binding protein in regulation of protein synthesis in mitosis. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 11134–11139. - PubMed
-
- Duncan R.F. (1996) Translational control during heat shock. In Hershey,J.W.B., Mathews,M.B. and Sonenberg,N. (eds), Translational Control During Heat Shock. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 271–294.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

