A geminivirus replication protein interacts with the retinoblastoma protein through a novel domain to determine symptoms and tissue specificity of infection in plants
- PMID: 10880461
- PMCID: PMC313951
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/19.13.3485
A geminivirus replication protein interacts with the retinoblastoma protein through a novel domain to determine symptoms and tissue specificity of infection in plants
Abstract
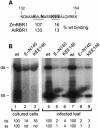
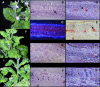
Geminiviruses replicate in nuclei of mature plant cells after inducing the accumulation of host DNA replication machinery. Earlier studies showed that the viral replication factor, AL1, is sufficient for host induction and interacts with the cell cycle regulator, retinoblastoma (pRb). Unlike other DNA virus proteins, AL1 does not contain the pRb binding consensus, LXCXE, and interacts with plant pRb homo logues (pRBR) through a novel amino acid sequence. We mapped the pRBR binding domain of AL1 between amino acids 101 and 180 and identified two mutants that are differentially impacted for AL1-pRBR interactions. Plants infected with the E-N140 mutant, which is wild-type for pRBR binding, developed wild-type symptoms and accumulated viral DNA and AL1 protein in epidermal, mesophyll and vascular cells of mature leaves. Plants inoculated with the KEE146 mutant, which retains 16% pRBR binding activity, only developed chlorosis along the veins, and viral DNA, AL1 protein and the host DNA synthesis factor, proliferating cell nuclear antigen, were localized to vascular tissue. These results established the importance of AL1-pRBR interactions during geminivirus infection of plants.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dual interaction of a geminivirus replication accessory factor with a viral replication protein and a plant cell cycle regulator.Virology. 2001 Jan 20;279(2):570-6. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0719. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11162812
-
A novel motif in geminivirus replication proteins interacts with the plant retinoblastoma-related protein.J Virol. 2004 May;78(9):4817-26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.9.4817-4826.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15078963 Free PMC article.
-
Geminivirus C3 protein: replication enhancement and protein interactions.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(15):9885-95. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.15.9885-9895.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16014949 Free PMC article.
-
Geminiviruses and the plant cell cycle.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Aug;43(5-6):763-72. doi: 10.1023/a:1006462028363. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 11089875 Review.
-
Geminiviruses: models for plant DNA replication, transcription, and cell cycle regulation.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2000;35(2):105-40. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10821479 Review.
Cited by
-
Geminivirus infection up-regulates the expression of two Arabidopsis protein kinases related to yeast SNF1- and mammalian AMPK-activating kinases.Plant Physiol. 2006 Dec;142(4):1642-55. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.088476. Epub 2006 Oct 13. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 17041027 Free PMC article.
-
Functional modulation of the geminivirus AL2 transcription factor and silencing suppressor by self-interaction.J Virol. 2007 Nov;81(21):11972-81. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00617-07. Epub 2007 Aug 22. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17715241 Free PMC article.
-
The Rep and C1 of Beet curly top Iran virus represent pathogenicity factors and induce hypersensitive response in Nicotiana benthamiana plants.Virus Genes. 2022 Dec;58(6):550-559. doi: 10.1007/s11262-022-01927-3. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Virus Genes. 2022. PMID: 35960462
-
Plant tumors: a hundred years of study.Planta. 2020 Mar 18;251(4):82. doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03375-5. Planta. 2020. PMID: 32189080 Review.
-
Recovery from virus infection: plant's armory in action.Planta. 2023 Apr 28;257(6):103. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04137-9. Planta. 2023. PMID: 37115475 Review.
References
-
- Bass H., Nagar,S., Hanley-Bowdoin,L. and Robertson,D. (2000) Chromosome condensation induced by geminivirus infection of mature plant cells. J. Cell Sci., 113, 1149–1160. - PubMed
-
- Chellappan S., Kraus,V.B., Kroger,B., Munger,K., Howley,P.M., Phelps,W.C. and Nevins,J.R. (1992) Adenovirus E1A, simian virus 40 tumor antigen and human papillomavirus E7 protein share the capacity to disrupt the interaction between transcription factor E2F and the retinoblastoma gene product. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 4549–4553. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

